DCs and NK cells: critical effectors in the immune response to HIV-1
- PMID: 21350578
- PMCID: PMC3278081
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2935
DCs and NK cells: critical effectors in the immune response to HIV-1
Abstract
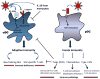
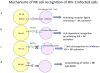
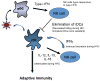
Dendritic cells (DCs) and natural killer (NK) cells have central roles in antiviral immunity by shaping the quality of the adaptive immune response to viruses and by mediating direct antiviral activity. HIV-1 infection is characterized by a severe dysregulation of the antiviral immune response that starts during early infection. This Review describes recent insights into how HIV-1 infection affects DC and NK cell function, and the roles of these innate immune cells in HIV-1 pathogenesis. The importance of understanding DC and NK cell crosstalk during HIV infection for the development of effective antiviral strategies is also discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Liu YJ. Dendritic cell subsets and lineages, and their functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell. 2001;106:259–62. - PubMed
-
- Rescigno M, Borrow P. The host-pathogen interaction: new themes from dendritic cell biology. Cell. 2001;106:267–70. - PubMed
-
- Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Regulation of T cell immunity by dendritic cells. Cell. 2001;106:263–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

