Fibroblast growth factors: biology, function, and application for tissue regeneration
- PMID: 21350642
- PMCID: PMC3042641
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/218142
Fibroblast growth factors: biology, function, and application for tissue regeneration
Abstract
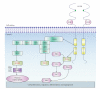
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) that signal through FGF receptors (FGFRs) regulate a broad spectrum of biological functions, including cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. The FGF signal pathways are the RAS/MAP kinase pathway, PI3 kinase/AKT pathway, and PLCγ pathway, among which the RAS/MAP kinase pathway is known to be predominant. Several studies have recently implicated the in vitro biological functions of FGFs for tissue regeneration. However, to obtain optimal outcomes in vivo, it is important to enhance the half-life of FGFs and their biological stability. Future applications of FGFs are expected when the biological functions of FGFs are potentiated through the appropriate use of delivery systems and scaffolds. This review will introduce the biology and cellular functions of FGFs and deal with the biomaterials based delivery systems and their current applications for the regeneration of tissues, including skin, blood vessel, muscle, adipose, tendon/ligament, cartilage, bone, tooth, and nerve tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110):920–926. - PubMed
-
- Hankemeier S, Keus M, Zeichen J, et al. Modulation of proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells by fibroblast growth factor 2: potential implications for tissue engineering of tendons and ligaments. Tissue Engineering. 2005;11(1-2):41–49. - PubMed
-
- Masukawa H, Miura Y, Sato I, Oiso Y, Suzuki A. Enhanced cartilage tissue engineering by sequential exposure of chondrocytes to FGF-2 during 2D expansion and BMP-2 during 3D cultivation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 2001;83(1):121–128. - PubMed
-
- Delgado-Rivera R, Harris SL, Ahmed I, et al. Increased FGF-2 secretion and ability to support neurite outgrowth by astrocytes cultured on polyamide nanofibrillar matrices. Matrix Biology. 2009;28(3):137–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

