A Parylene MEMS Electrothermal Valve
- PMID: 21350679
- PMCID: PMC3042720
- DOI: 10.1109/JMEMS.2009.2031689
A Parylene MEMS Electrothermal Valve
Abstract
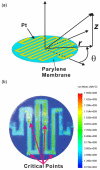
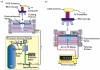
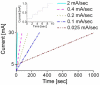
The first microelectromechanical-system normally closed electrothermal valve constructed using Parylene C is described, which enables both low power (in milliwatts) and rapid operation (in milliseconds). This low-power valve is well suited for applications in wirelessly controlled implantable drug-delivery systems. The simple design was analyzed using both theory and modeling and then characterized in benchtop experiments. Operation in air (constant current) and water (current ramping) was demonstrated. Valve-opening powers of 22 mW in air and 33 mW in water were obtained. Following integration of the valve with catheters, our valve was applied in a wirelessly operated microbolus infusion pump, and the in vivo functionality for the appropriateness of use of this pump for future brain mapping applications in small animals was demonstrated.
Figures













References
-
- Li P-Y, Givrad TK, Holschneider DP, Maarek J-MI, Meng E. A wirelessly-activated Parylene electrothermal valve for mapping brain function in freely moving subjects; presented at the Solid-State Sensors, Actuators, Microsystems Workshop; Hilton Head Island, SC. 2008.
-
- Meng E, Li P-Y, Tai Y-C. A biocompatible Parylene thermal flow sensing array. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 2008 May;144(1):18–28.
-
- Li P-Y, Shih J, Lo R, Saati S, Agrawal R, Humayun MS, Tai Y-C, Meng E. An electrochemical intraocular drug delivery device. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 2008 May;143(1):41–48.
-
- Maloney JM, Uhland SA, Polito BF, Sheppard NF, Jr., Pelta CM, Santini JT., Jr. Electrothermally activated microchips for implantable drug delivery and biosensing. J. Control. Release. 2005 Dec.109(1–3):244–255. - PubMed
-
- Cardenas-Valencia AM, Dlutowski J, Bumgarner J, Munoz C, Wang W, Popuri R, Langebrake L. Development of various designs of low-power MEMS valves for fluidic applications. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 2007 May;136(1):374–384.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
