Functional analysis of microRNAs in human hepatocellular cancer stem cells
- PMID: 21352471
- PMCID: PMC3116063
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01282.x
Functional analysis of microRNAs in human hepatocellular cancer stem cells
Abstract
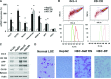
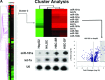
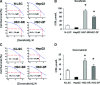
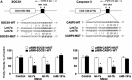
MicroRNAs are endogenous small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression and cancer development. A rare population of hepatocellular cancer stem cells (HSCs) holds the extensive proliferative and self-renewal potential necessary to form a liver tumour. We postulated that specific transcriptional factors might regulate the expression of microRNAs and subsequently modulate the expression of gene products involved in phenotypic characteristics of HSCs. We evaluated the expression of microRNA in human HSCs by microarray profiling, and defined the target genes and functional effects of two groups of microRNA regulated by IL-6 and transcriptional factor Twist. A subset of highly chemoresistant and invasive HSCs was screened with aberrant expressions of cytokine IL-6 and Twist. We demonstrated that conserved let-7 and miR-181 family members were up-regulated in HSCs by global microarray-based microRNA profiling followed by validation with real-time polymerase chain reaction. Importantly, inhibition of let-7 increases the chemosensitivity of HSCs to sorafenib and doxorubicin whereas silencing of miR-181 led to a reduction in HSCs motility and invasion. Knocking down IL-6 and Twist in HSCs significantly reduced let-7 and miR-181 expression and subsequently inhibited chemoresistance and cell invasion. We showed that let-7 directly targets SOCS-1 and caspase-3, whereas miR-181 directly targets RASSF1A, TIMP3 as well as nemo-like kinase (NLK). In conclusion, alterations of IL-6- and Twist-regulated microRNA expression in HSCs play a part in tumour spreading and responsiveness to chemotherapy. Our results define a novel regulatory mechanism of let-7/miR-181s suggesting that let-7 and miR-181 may be molecular targets for eradication of hepatocellular malignancies.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




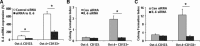

References
-
- Adams JM, Strasser A. Is tumor growth sustained by rare cancer stem cells or dominant clones? Cancer Res. 2008;68:4018–21. - PubMed
-
- Rosa A, Brivanlou AH. microRNAs in early vertebrate development. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:3513–20. - PubMed
-
- Sartipy P, Olsson B, Hyllner J, Synnergren J. Regulation of ‘stemness’ and stem cell differentiation by microRNAs. IDrugs. 2009;12:492–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

