Normalization of proliferation and tight junction formation in bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by d-proline and d-pipecolic acid derivatives of antiproliferative factor
- PMID: 21352500
- PMCID: PMC7213761
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01108.x
Normalization of proliferation and tight junction formation in bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by d-proline and d-pipecolic acid derivatives of antiproliferative factor
Abstract
Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome is a chronic bladder disorder with epithelial thinning or ulceration, pain, urinary frequency and urgency, for which there is no reliably effective therapy. We previously reported that interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome bladder epithelial cells make a glycopeptide antiproliferative factor or 'APF' (Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAcα-O-TVPAAVVVA) that induces abnormalities in normal cells similar to those in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome cells in vitro, including decreased proliferation, decreased tight junction formation, and increased paracellular permeability. We screened inactive APF derivatives for their ability to block antiproliferative activity of asialylated-APF ('as-APF') in normal bladder cells and determined the ability of as-APF-blocking derivatives to normalize tight junction protein expression, paracellular permeability, and/or proliferation of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome cells. Only two of these derivatives [Galβ1-3GalNAcα-O-TV-(d-pipecolic acid)-AAVVVA and Galβ1-3GalNAcα-O-TV-(d-proline)-AAVVVA] blocked as-APF antiproliferative activity in normal cells (p < 0.001 for both). Both of these antagonists also 1) significantly increased mRNA expression of ZO-1, occludin, and claudins 1, 4, 8, and 12 in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome cells by qRT-PCR; 2) normalized interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome epithelial cell tight junction protein expression and tight junction formation by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy; and 3) decreased paracellular permeability of (14) C-mannitol and (3) H-inulin between confluent interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome epithelial cells on Transwell plates, suggesting that these potent APF antagonists may be useful for the development as interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome therapies.
Published 2011. This article is a US Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a conflict of interest related to the work described in this manuscript.
Figures
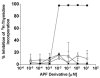
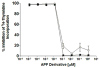

 ), inactive peptide (
), inactive peptide (
 ), or diluent control (■) twice weekly, and RNA was extracted at 9, 16, 23 and 30 days for qRT-PCR. By day 16, both APF derivatives were able to significantly (p < .05) stimulate tight junction protein expression in IC/PBS cells in vitro resulting in levels similar to those seen in bladder cells from age- and gender-matched normal donors (
), or diluent control (■) twice weekly, and RNA was extracted at 9, 16, 23 and 30 days for qRT-PCR. By day 16, both APF derivatives were able to significantly (p < .05) stimulate tight junction protein expression in IC/PBS cells in vitro resulting in levels similar to those seen in bladder cells from age- and gender-matched normal donors (
 ). PCR was performed in duplicate on three separate occasions for each sample; data are expressed as mean +/- standard error of the mean. (Data shown from experiment with the same IC/PBS cell donor treated simultaneously with either
). PCR was performed in duplicate on three separate occasions for each sample; data are expressed as mean +/- standard error of the mean. (Data shown from experiment with the same IC/PBS cell donor treated simultaneously with either 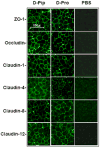
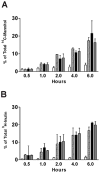
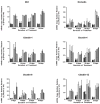
 ), diluent control (■), or calcium free medium (
), diluent control (■), or calcium free medium (
 ) for 16 days prior to incubation with tracer. Data are expressed as mean percent of the radioactivity applied to the apical medium that was recovered in the basal medium at 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hrs, 4 hrs, 6 hrs +/- standard deviation. (Data shown from 4 experiments using cells from 4 different IC/PBS donors).
) for 16 days prior to incubation with tracer. Data are expressed as mean percent of the radioactivity applied to the apical medium that was recovered in the basal medium at 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hrs, 4 hrs, 6 hrs +/- standard deviation. (Data shown from 4 experiments using cells from 4 different IC/PBS donors).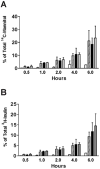
 ), diluent control (■), or calcium free medium (
), diluent control (■), or calcium free medium (
 ) for 16 days prior to incubation with tracer. Data are expressed as mean percent of the radioactivity applied to the apical medium that was recovered in the basal medium at 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hrs, 4 hrs, 6 hrs +/- standard deviation. (Data shown from 3 experiments using cells from 3 different IC/PBS donors).
) for 16 days prior to incubation with tracer. Data are expressed as mean percent of the radioactivity applied to the apical medium that was recovered in the basal medium at 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hrs, 4 hrs, 6 hrs +/- standard deviation. (Data shown from 3 experiments using cells from 3 different IC/PBS donors).Comment in
-
Re: Normalization of proliferation and tight junction formation in bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by d-proline and d-pipecolic acid derivatives of antiproliferative factor.J Urol. 2011 Dec;186(6):2264-5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.148. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 22078590 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johansson SL, Fall M. Clinical features and spectrum of light microscopic changes in interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 1990;143:1118–1124. - PubMed
-
- Skoluda D, Wegner K, Lemmel EM. Critical Notes: Respective immune pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis. (article in German) Urologe A. 1974;13:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Tomaszewski JE, Landis JR, Russack V, Williams TM, Wang LP, Hardy C, Brensinger C, Matthews YL, Abele ST, Kusek JW, Nyberg LM. Biopsy features are associated with primary symptoms in interstitial cystitis: results from the Interstitial Cystitis Database Study Group. Urology. 2001;57:67–81. - PubMed
-
- Lavelle J, Meyers S, Ramage R, Bastacky S, Doty D, Apodaca G, Zeidel ML. Bladder permeability barrier: recovery from selective injury of surface epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;283:F242–F253. - PubMed
-
- Acharya P, Beckel J, Ruiz WG, Wang E, Rojas R, Birder L, Apodaca G. Distribution of the tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-4, -8, and -12 in bladder epithelium. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:F305–F318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

