Differentiation of canine distemper virus isolates in fur animals from various vaccine strains by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism according to phylogenetic relations in china
- PMID: 21352564
- PMCID: PMC3056815
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-85
Differentiation of canine distemper virus isolates in fur animals from various vaccine strains by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism according to phylogenetic relations in china
Abstract
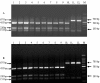
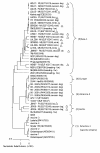
In order to effectively identify the vaccine and field strains of Canine distemper virus (CDV), a new differential diagnostic test has been developed based on reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). We selected an 829 bp fragment of the nucleoprotein (N) gene of CDV. By RFLP analysis using BamHI, field isolates were distinguishable from the vaccine strains. Two fragments were obtained from the vaccine strains by RT-PCR-RFLP analysis while three were observed in the field strains. An 829 nucleotide region of the CDV N gene was analyzed in 19 CDV field strains isolated from minks, raccoon dogs and foxes in China between 2005 and 2007. The results suggest this method is precise, accurate and efficient. It was also determined that three different genotypes exist in CDV field strains in fur animal herds of the north of China, most of which belong to Asian type. Mutated field strains, JSY06-R1, JSY06-R2 and JDH07-F1 also exist in Northern China, but are most closely related to the standard virulent strain A75/17, designated in Arctic and America-2 genetype in the present study, respectively.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander KA, Appel MJ. African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) endangered by a canine distemper epizootic among domestic dogs near the Masai Mara National Reserve, Kenya. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30(4):481–485. - PubMed
-
- Mainka SA, Qiu X, He T, Appel MJ. Serologic survey of giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca), and domestic dogs and cats in the Wolong Reserve, China. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30(1):86–89. - PubMed
-
- Monson RA, Stone WB. Canine distemper in wild carnivores in New York. N Y Fish Game J. 1976;23(2):149–154.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

