Revised cutoff values of ALT and HBV DNA level can better differentiate HBeAg (-) chronic inactive HBV patients from active carriers
- PMID: 21352567
- PMCID: PMC3052190
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-86
Revised cutoff values of ALT and HBV DNA level can better differentiate HBeAg (-) chronic inactive HBV patients from active carriers
Abstract
Background and aims: ELISA is still used as primary test for diagnosis HBV disease. However, ELISA-positive patients were marked as HBV inactive after confirmation with PCR and vice versa. Our aim was to assess the performance of new cut-off value of ALT, HBV DNA load and significance of AST as screening tool for HBeAg (-) chronic active or inactive patients in Pakistani population.
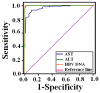
Materials and methods: In a cross-sectional, cohort study, 567 HBeAg (-) patients followed for one year were selected. Patients with persistent elevated ALT than normal and HBV DNA ≥ 100,000 copies/mL were taken as active chronic. Diagnostic values for ALT, AST and HBV DNA load in HBV HBeAg (-) chronic active and inactive patients compared using receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curves.
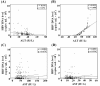
Results: Of 567 HBeAg (-) patients, 228 were classified as chronic inactive and 339 as active. HBV infection was dominant in male. Serum ALT, AST and HBV DNA levels showed significant and high AUROC to differentiate chronic HBeAg (-) inactive patients from active. AUROC for Serum ALT, AST and HBV DNA were observed 0.997, 0.969 and 1.000, respectively. For revised cut off value for ALT (30 IU/L for male and 19 IU/L for female) and HBV DNA load ≥100,000 copies/mL, a PPV of 97%, NPV of 94%, a sensitivity of 98%, and a specificity of 92% was observed to discriminate active carriers from inactive carriers. We also observed 93.5% specificity, 83.1% sensitivity, 82% PPV and 89.5% NPV for AST ≤20 IU/L to differentiate inactive carriers from active ones in our study group.
Conclusions: Revised cut off value of ALT and NIH derived HBV DNA value can better discriminate between HBeAg (-) chronic active and inactive patients.
Figures
References
-
- Buti M, Sanchez F, Cotrina M, Jardi R, Rodriguez F, Esteban R, Guardia J. Quantitative hepatitis B virus DNA testing for the early prediction of the maintenance of response during lamivudine therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1277–1280. doi: 10.1086/319677. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

