Lung ultrasound: a new tool for the cardiologist
- PMID: 21352576
- PMCID: PMC3059291
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-9-6
Lung ultrasound: a new tool for the cardiologist
Abstract
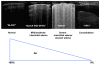
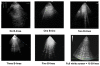
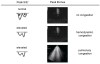
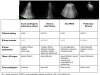
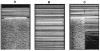
For many years the lung has been considered off-limits for ultrasound. However, it has been recently shown that lung ultrasound (LUS) may represent a useful tool for the evaluation of many pulmonary conditions in cardiovascular disease. The main application of LUS for the cardiologist is the assessment of B-lines. B-lines are reverberation artifacts, originating from water-thickened pulmonary interlobular septa. Multiple B-lines are present in pulmonary congestion, and may help in the detection, semiquantification and monitoring of extravascular lung water, in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea, and in the prognostic stratification of chronic heart failure and acute coronary syndromes.
Figures

References
-
- Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 17. New York, McGraw-Hill; 2008.
-
- Lichtenstein DA. General Ultrasound in the Critically Ill. II. Berlin, Springer Verlag; 2007.
-
- Ziskin MC, Thickman DI, Goldenberg NJ, Lapayowker MS, Becker JM. The comet tail artifact. J Ultrasound Med. 1982;1:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Thickman DI, Ziskin MC, Goldenberg NJ, Linder BE. Clinical manifestations of the comet tail artifact. J Ultrasound Med. 1983;2:225–30. - PubMed
-
- Targhetta R, Chavagneux R, Balmes P, Lemerre C, Mauboussin JM, Bourgeois JM, Pourcelot L. Sonographic lung surface evaluation in pulmonary sarcoidosis: preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med. 1994;13:381–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

