Glial NF-κB inhibition alters neuropeptide expression after sciatic nerve injury in mice
- PMID: 21352816
- PMCID: PMC4292841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.055
Glial NF-κB inhibition alters neuropeptide expression after sciatic nerve injury in mice
Abstract
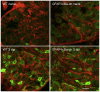
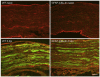
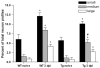
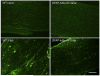
We utilized a transgenic mouse model where nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is selectively inhibited in glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expressing cells. The transgene, GFAP-IκBα-dn, overexpresses a dominant negative form of the inhibitor of NF-κB (IκBα) under the control of the GFAP promoter. In the present work, we sought to understand the impact of glial NF-κB inhibition on the expression of pain mediating sensory neuropeptides galanin and calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) in a model of neuropathic pain in mice. Chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the left sciatic nerve was performed on wild type (WT) and GFAP-IκBα-dn transgenic mice. RT-PCR and immunohistological staining were performed in sciatic nerve and/or L4-L5 DRG tissue for galanin, CGRP and macrophage marker CD11b. GFAP-IκBα-dn mice had less mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia compared to WT mice post-CCI. After CCI, we observed galanin upregulation in DRG and sciatic nerve, which was less in GFAP-IκBα-dn mice. CGRP gene expression in the DRG increased transiently on day 1 post-CCI in WT but not in GFAP-IκBα-dn mice, and no evidence of CGRP upregulation in sciatic nerve post-CCI was found. After CCI, upregulation of CD11b in sciatic nerve was less in GFAP-IκBα-dn mice compared to WT mice, indicative of less macrophage infiltration. Our results showed that glial NF-κB inhibition reduces galanin and CGRP expression, which are neuropeptides that correlate with pain behavior and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
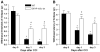
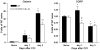
Similar articles
-
Transgenic inhibition of glial NF-kappa B reduces pain behavior and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury.Pain. 2010 Mar;148(3):509-518. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Pain. 2010. PMID: 20097004 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic effects of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway inhibition on chronic neuropathic pain in rats following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:526-533. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.116. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. Retraction in: Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114724. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114724. PMID: 30114636 Retracted.
-
Phenotyping of sensory and sympathetic ganglion neurons of a galanin-overexpressing mouse--possible implications for pain processing.J Chem Neuroanat. 2006 Jun;31(4):243-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2006.02.001. Epub 2006 Mar 20. J Chem Neuroanat. 2006. PMID: 16546349
-
Ameliorative effects of escin on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113503. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113503. Epub 2020 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33091488
-
Use of genetically engineered transgenic mice to investigate the role of galanin in the peripheral nervous system after injury.Neuropeptides. 2005 Jun;39(3):191-9. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2005.01.001. Neuropeptides. 2005. PMID: 15944011 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of astrocytic NF-κB on healthy and Alzheimer's disease brains.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 21;14(1):14305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65248-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38906984 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-κB protects from optic nerve damage and retinal ganglion cell loss in experimental optic neuritis.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Sep 10;9:213. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-213. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22963651 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain-induced depressive-like behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis and plasticity are dependent on TNFR1 signaling.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Oct;41:65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24938671 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Factor κB-COX2 Pathway Activation in Non-myelinating Schwann Cells Is Necessary for the Maintenance of Neuropathic Pain in vivo.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 14;15:782275. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.782275. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095422 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte D-serine modulates the activation of neuronal NOS leading to the development of mechanical allodynia in peripheral neuropathy.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919843046. doi: 10.1177/1744806919843046. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 30900515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Biella G, Panara C, Pecile A, Sotgiu ML. Facilitatory role of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on excitation induced by substance P (SP) and noxious stimuli in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. An iontophoretic study in vivo. Brain Res. 1991;559:352–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

