Local modulation of striatal glutamate efflux by serotonin 1A receptor stimulation in dyskinetic, hemiparkinsonian rats
- PMID: 21352823
- PMCID: PMC3100430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.02.012
Local modulation of striatal glutamate efflux by serotonin 1A receptor stimulation in dyskinetic, hemiparkinsonian rats
Abstract
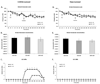
Serotonin 1A receptor (5-HT(1A)R) agonists reduce both L-DOPA- and D1 receptor (D1R) agonist-mediated dyskinesia, but their anti-dyskinetic mechanism of action is not fully understood. Given that 5-HT(1A)R stimulation reduces glutamatergic neurotransmission in the dopamine-depleted striatum, 5-HT(1A)R agonists may diminish dyskinesia in part through modulation of pro-dyskinetic striatal glutamate levels. To test this, rats with unilateral medial forebrain bundle dopamine or sham lesions were primed with L-DOPA (12 mg/kg+benserazide, 15 mg/kg, sc) or the D1R agonist SKF81297 (0.8 mg/kg, sc) until abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) stabilized. On subsequent test days, rats were treated with vehicle or the 5-HT(1A)R agonist ±8-OH-DPAT (1.0 mg/kg, sc), followed by L-DOPA or SKF81297, or intrastriatal ±8-OH-DPAT (7.5 or 15 mM), followed by L-DOPA. In some cases, the 5-HT(1A)R antagonist WAY100635 was employed to determine receptor-specific effects. In vivo microdialysis was used to collect striatal samples for analysis of extracellular glutamate levels during AIMs assessment. Systemic and striatal ±8-OH-DPAT attenuated L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and striatal glutamate efflux while WAY100635 reversed ±8-OH-DPAT's effects. Interestingly, systemic ±8-OH-DPAT diminished D1R-mediated AIMs without affecting glutamate. These findings indicate a novel anti-dyskinetic mechanism of action for 5-HT(1A)R agonists with implications for the improved treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
5-HT(1A) receptor stimulation and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: bridging the gap between serotonergic and glutamatergic mechanisms.Exp Neurol. 2011 Oct;231(2):195-8. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.07.006. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Exp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21819982 No abstract available.
References
-
- Antonelli T, Fuxe K, Tomasini MC, Bartoszyk GD, Seyfried CA, Tanganelli S, Ferraro L. Effects of sarizotan on the corticostriatal glutamate pathways. Synapse. 2005;58:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Guigoni C, Hakansson K, et al. Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann. Neurol. 2005;57:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Bara-Jimenez W, Bibbiani F, Morris MJ, Dimitrova T, Sherzai A, Mouradian MM, Chase TN. Effects of serotonin 5-HT1A agonist in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2005;20:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi L, Galeffi F, Bolam JP, Della Corte L. The effect of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions on the release of amino acids in the direct and indirect pathways of the basal ganglia: A dual microdialysis probe analysis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003;18:856–868. - PubMed
-
- Bibbiani F, Oh JD, Kielaite A, Collins MA, Smith C, Chase TN. Combined blockade of AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors reduces levodopa-induced motor complications in animal models of PD. Exp. Neurology. 2005;196:422–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

