Ancylostoma ceylanicum excretory-secretory protein 2 adopts a netrin-like fold and defines a novel family of nematode proteins
- PMID: 21352830
- PMCID: PMC3070796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.02.033
Ancylostoma ceylanicum excretory-secretory protein 2 adopts a netrin-like fold and defines a novel family of nematode proteins
Abstract
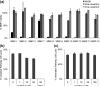
Hookworms are human parasites that have devastating effects on global health, particularly in underdeveloped countries. Ancylostoma ceylanicum infects humans and animals, making it a useful model organism to study disease pathogenesis. A. ceylanicum excretory-secretory protein 2 (AceES-2), a highly immunoreactive molecule secreted by adult worms at the site of intestinal attachment, is partially protective when administered as a mucosal vaccine against hookworm anemia. The crystal structure of AceES-2 determined at 1.75 Å resolution shows that it adopts a netrin-like fold similar to that found in tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteases (TIMPs) and in complement factors C3 and C5. However, recombinant AceES-2 does not significantly inhibit the 10 most abundant human matrix metalloproteases or complement-mediated cell lysis. The presence of a highly acidic surface on AceES-2 suggests that it may function as a cytokine decoy receptor. Several small nematode proteins that have been annotated as TIMPs or netrin-domain-containing proteins display sequence homology in structurally important regions of AceES-2's netrin-like fold. Together, our results suggest that AceES-2 defines a novel family of nematode netrin-like proteins, which may function to modulate the host immune response to hookworm and other parasites.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
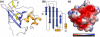
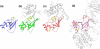

References
-
- Hotez PJ, Brooker S, Bethony JM, Bottazzi ME, Loukas A, Xiao S. Hookworm infection. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:799–807. - PubMed
-
- Loukas A, Constant SL, Bethony JM. Immunobiology of hookworm infection. Fems Immunology and Medical Microbiology. 2005;43:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Maizels RM, Yazdanbakhsh M. Immune regulation by helminth parasites: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2003;3:733–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

