Regulation of axonal mitochondrial transport and its impact on synaptic transmission
- PMID: 21352858
- PMCID: PMC3086944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neures.2011.02.005
Regulation of axonal mitochondrial transport and its impact on synaptic transmission
Abstract
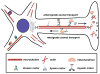
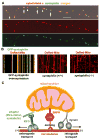
Mitochondria are essential organelles for neuronal survival and play important roles in ATP generation, calcium buffering, and apoptotic signaling. Due to their extreme polarity, neurons utilize specialized mechanisms to regulate mitochondrial transport and retention along axons and near synaptic terminals where energy supply and calcium homeostasis are in high demand. Axonal mitochondria undergo saltatory and bidirectional movement and display complex mobility patterns. In cultured neurons, approximately one-third of axonal mitochondria are mobile, while the rest remain stationary. Stationary mitochondria at synapses serve as local energy stations that produce ATP to support synaptic function. In addition, axonal mitochondria maintain local Ca²+ homeostasis at presynaptic boutons. The balance between mobile and stationary mitochondria is dynamic and responds quickly to changes in axonal and synaptic physiology. The coordination of mitochondrial mobility and synaptic activity is crucial for neuronal function synaptic plasticity. In this update article, we introduce recent advances in our understanding of the motor-adaptor complexes and docking machinery that mediate mitochondrial transport and axonal distribution. We will also discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying the complex mobility patterns of axonal mitochondria and how mitochondrial mobility impacts the physiology and function of synapses.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial transport and docking in axons.Exp Neurol. 2009 Aug;218(2):257-67. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.03.024. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19341731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motile axonal mitochondria contribute to the variability of presynaptic strength.Cell Rep. 2013 Aug 15;4(3):413-419. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.040. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23891000 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mitochondrial transport in neurons.Exp Cell Res. 2015 May 15;334(1):35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25612908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Docking of axonal mitochondria by syntaphilin controls their mobility and affects short-term facilitation.Cell. 2008 Jan 11;132(1):137-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.024. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18191227 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial trafficking and anchoring in neurons: New insight and implications.J Cell Biol. 2014 Mar 31;204(7):1087-98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201312123. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24687278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chain length of saturated fatty acids regulates mitochondrial trafficking and function in sensory neurons.J Lipid Res. 2019 Jan;60(1):58-70. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M086843. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30442656 Free PMC article.
-
Technologies to Study Action Potential Propagation With a Focus on HD-MEAs.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Apr 26;13:159. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00159. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31118887 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Nrf2 Pathway on Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Failure in Parkinson and Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;10(7):1069. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071069. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connecting mitochondrial dynamics and life-or-death events via Bcl-2 family proteins.Neurochem Int. 2017 Oct;109:141-161. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Neurochem Int. 2017. PMID: 28461171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MERCs. The Novel Assistant to Neurotransmission?Front Neurosci. 2020 Nov 9;14:589319. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.589319. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33240039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

