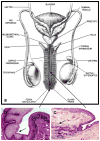
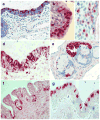
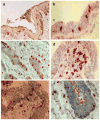
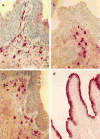
Innate and acquired immunity in the human penile urethra
- PMID: 21353311
- PMCID: PMC3065209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.01.006
Innate and acquired immunity in the human penile urethra
Abstract
In men, the penile urethra is a primary infection site for sexually transmitted pathogens. Research on the immunology of this mucosal site has been limited in part due to sampling challenges, but available evidence indicates that the urethra contains a rich contingent of immunological mediators that can mount vigorous innate and adaptive immune responses against infectious organisms. Further research is needed to define approaches to stimulate immunity at this mucosal site to prevent the transmission of HIV-1 and other sexually transmitted pathogens.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- CERF-BENSUSSAN N, JARRY A, BROUSSE N, LISOWSKA-GROSPIERRE B, GRISCELLI C, GUY-GRAND D. Monoclonal antibodies specific for human and rat intestinal lymphocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216A:483–91. - PubMed
-
- COLE AM. Innate host defense of human vaginal and cervical mucosae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;306:199–230. - PubMed
-
- DEKKER J, ROSSEN JW, BULLER HA, EINERHAND AW. The MUC family: an obituary. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27:126–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

