Kinetic analysis reveals the fate of a microRNA following target regulation in mammalian cells
- PMID: 21353554
- PMCID: PMC3088433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.01.067
Kinetic analysis reveals the fate of a microRNA following target regulation in mammalian cells
Abstract
Considerable details about microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis and regulation have been uncovered, but little is known about the fate of the miRNA subsequent to target regulation. To gain insight into this process, we carried out kinetic analysis of a miRNA's turnover following termination of its biogenesis and during regulation of a target that is not subject to Ago2-mediated catalytic cleavage. By quantitating the number of molecules of the miRNA and its target in steady state and in the course of its decay, we found that each miRNA molecule was able to regulate at least two target transcripts, providing in vivo evidence that the miRNA is not irreversibly sequestered with its target and that the nonslicing pathway of miRNA regulation is multiple-turnover. Using deep sequencing, we further show that miRNA recycling is limited by target regulation, which promotes posttranscriptional modifications to the 3' end of the miRNA and accelerates the miRNA's rate of decay. These studies provide new insight into the efficiency of miRNA regulation that help to explain how a miRNA can regulate a vast number of transcripts and that identify one of the mechanisms that impart specificity to miRNA decay in mammalian cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
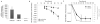
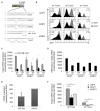


Comment in
-
Small RNAs: Recycling for silencing.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Apr;12(4):227. doi: 10.1038/nrg2977. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21403677 No abstract available.
References
-
- Krol J, Busskamp V, Markiewicz I, Stadler MB, Ribi S, et al. Characterizing light-regulated retinal microRNAs reveals rapid turnover as a common property of neuronal microRNAs. Cell. 2010;141:618–631. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S, Grosshans H. Active turnover modulates mature microRNA activity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2009;461:546–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

