Passive immunoprotection targeting a secreted CAMP factor of Propionibacterium acnes as a novel immunotherapeutic for acne vulgaris
- PMID: 21354482
- PMCID: PMC3388602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.02.036
Passive immunoprotection targeting a secreted CAMP factor of Propionibacterium acnes as a novel immunotherapeutic for acne vulgaris
Abstract
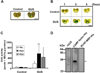
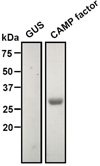
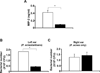
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria play a key role in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. Although our previous studies have demonstrated that vaccines targeting a surface sialidase or bacterial particles exhibit a preventive effect against P. acnes, the lack of therapeutic activities and incapability of neutralizing secretory virulence factors motivate us to generate novel immunotherapeutics. In this study, we develop an immunotherapeutic antibody to secretory Christie-Atkins-Munch-Peterson (CAMP) factor of P. acnes. Via agroinfiltration, P. acnes CAMP factor was encapsulated into the leaves of radishes. ICR mice intranasally immunized with whole leaves expressing CAMP factor successfully produced neutralizing antibodies that efficiently attenuated P. acnes-induced ear swelling and production of macrophage-inflammatory protein-2. Passive neutralization of CAMP factor enhanced immunity to eradicate P. acnes at the infection site without influencing bacterial growth elsewhere. We propose that CAMP factor is a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of various P. acnes-associated diseases and highlight the concept of neutralizing P. acnes virulence without disturbing the bacterial commensalism in human microbiome.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Dekio I, Sakamoto M, Hayashi H, Amagai M, Suematsu M, Benno Y. Characterization of skin microbiota in patients with atopic dermatitis and in normal subjects using 16S rRNA gene-based comprehensive analysis. J Med Microbiol. 2007;56(Pt 12):1675–1683. - PubMed
-
- Brook I, Frazier EH. Infections caused by Propionibacterium species. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13(5):819–822. - PubMed
-
- Ahn CY, Ko CY, Wagar EA, Wong RS, Shaw WW. Microbial evaluation: 139 implants removed from symptomatic patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;98(7):1225–1229. - PubMed
-
- Tancrede C. Role of human microflora in health and disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;11(11):1012–1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

