Reconstitutable charged polymeric (PLGA)(2)-b-PEI micelles for gene therapeutics delivery
- PMID: 21354616
- PMCID: PMC3073820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.077
Reconstitutable charged polymeric (PLGA)(2)-b-PEI micelles for gene therapeutics delivery
Abstract
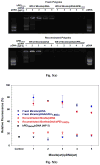
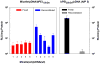
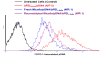
This study investigated the potential of creating a charged polymeric micelle-based nucleic acid delivery system that could easily be reconstituted by the addition of water. (PLGA(36kDa))(2)-b-bPEI(25kDa) (PLGA MW 36 kDa, bPEI M(w) 25 kDa, PLGA:bPEI block ratio = 2) was synthesized and used to prepare cationic micelles. The copolymer retained proton-buffering capability from the bPEI block within the endosomal pH range. Micelle/pDNA complexes retained their particle size (100-150 nm) and surface charge (30-40 mV) following reconstitution. It was found that adding a small amount of low molecular weight bPEI (1.8 kDa) completely shielded pDNA in the micelle/pDNA complexes and enhanced transfection efficiency 50-100 fold for both fresh and reconstituted complexes without affecting complex size. Transfection efficiency for "reconstituted" micelle/pDNA/bPEI(1.8kDa) (WR 1) complexes was 16-fold higher than its "fresh" counterpart. Although transfection levels achieved using "reconstituted" micelle/pDNA/bPEI(1.8kDa) complexes were 3.6-fold lower than control "fresh" bPEI(25kDa)/pDNA (N/P 5) complexes, transfection levels were 39-fold higher than "reconstituted" bPEI(25kDa)/pDNA (N/P 5) complexes. The micelle/pDNA/bPEI(1.8kDa) system showed very low cytotoxicity in MCF7 cells even with pDNA doses up to 20 μg, and transfection levels increased linearly with increasing pDNA dose. These results indicate that this PLGA-b-bPEI polymeric micelle-based system is well suited as a reconstitutable gene delivery system, and has high potential for use as a delivery system for gene therapy applications.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Nanoscaled buffering zone of charged (PLGA)n-b-bPEI micelles in acidic microclimate for potential protein delivery application.J Control Release. 2012 Jun 28;160(3):440-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.02.024. Epub 2012 Mar 3. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22405902 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic, amphiphilic copolymer micelles as nucleic acid carriers for enhanced transfection in rat spinal cord.Acta Biomater. 2016 Apr 15;35:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 26873365 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone-loaded reconstitutable charged polymeric (PLGA)n -b-bPEI micelles for enhanced nuclear delivery of gene therapeutics.Macromol Biosci. 2014 Jun;14(6):831-41. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201300432. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Macromol Biosci. 2014. PMID: 24550091
-
A reducible polycationic gene vector derived from thiolated low molecular weight branched polyethyleneimine linked by 2-iminothiolane.Biomaterials. 2011 Feb;32(4):1193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.079. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21071079 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design, fabrication, characterization and in vitro testing of biodegradable microparticles that generate targeted and sustained transgene expression in HepG2 liver cells.J Drug Target. 2011 Jul;19(6):393-408. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2010.504263. Epub 2010 Aug 3. J Drug Target. 2011. PMID: 20681752 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physicochemical stability and transfection efficiency of cationic amphiphilic copolymer/pDNA polyplexes for spinal cord injury repair.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 12;7(1):11247. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10982-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28900263 Free PMC article.
-
[Synthesis of amphiphilic block copolymer of PLGA-b-(PEI-co-PEG) and characterization of the self-assembled cationic micelles].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018 Aug 30;38(9):1139-1146. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.09.20. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 30377107 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Multifunctional unimolecular micelles for cancer-targeted drug delivery and positron emission tomography imaging.Biomaterials. 2012 Apr;33(11):3071-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.12.030. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22281424 Free PMC article.
-
A Multilayered Cell Culture Model for Transport Study in Solid Tumors: Evaluation of Tissue Penetration of Polyethyleneimine Based Cationic Micelles.Nano Today. 2014 Dec 1;9(6):695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.10.003. Nano Today. 2014. PMID: 25866552 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Active Tumor Targeted Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Combination Chemotherapy in Cancer Treatment and Imaging.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015 Nov;11(11):1859-98. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2015.2145. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26554150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- López-Fraga M, Wright N, Jiménez A. RNA interference-based therapeutics: new strategies to fight infectious disease. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2008;8:262–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

