Sam68 marks the transcriptionally active stages of spermatogenesis and modulates alternative splicing in male germ cells
- PMID: 21355037
- PMCID: PMC3130265
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr085
Sam68 marks the transcriptionally active stages of spermatogenesis and modulates alternative splicing in male germ cells
Abstract
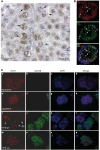
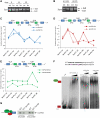
Sam68 plays an essential role in mouse spermatogenesis and male fertility. Herein, we report an interaction between Sam68 and the phosphorylated forms of the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) in meiotic spermatocytes. RNase treatment decreased but did not abolish the interaction, consistently with in vitro binding of RNAPII to the Sam68 carboxyl-terminal region. Sam68 retention in the spermatocyte nucleus was dependent on the integrity of cellular RNAs, suggesting that the protein is recruited to transcriptionally active chromatin. Mouse knockout models characterized by stage-specific arrest of spermatogenesis and staining with the phosphorylated form of RNAPII documented that Sam68 expression is confined to the transcriptionally active stages of spermatogenesis. Furthermore, Sam68 associates with splicing regulators in germ cells and we report that alternative splicing of Sgce exon 8 is regulated in a Sam68-dependent manner during spermatogenesis. RNA and chromatin crosslink immunoprecipitation experiments showed that Sam68 binds in vivo to sequences surrounding the intron 7/exon 8 boundary, thereby affecting the recruitment of the phosphorylated RNAPII and of the general splicing factor U2AF65. These results suggest that Sam68 regulates alternative splicing at transcriptionally active sites in differentiating germ cells and provide new insights into the regulation of Sam68 expression during spermatogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Braun RE. Post-transcriptional control of gene expression during spermatogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998;9:483–489. - PubMed
-
- Elliott D. Pathways of post-transcriptional gene regulation in mammalian germ cell development. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003;103:210–216. - PubMed
-
- Paronetto MP, Sette C. Role of RNA-binding proteins in mammalian spermatogenesis. Int. J. Androl. 2010;33:2–12. - PubMed
-
- Turner JM, Mahadevaiah SK, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Nussenzweig A, Xu X, Deng CX, Burgoyne PS. Silencing of unsynapsed meiotic chromosomes in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:41–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

