Activation of PI3-kinase stimulates endocytosis of ROMK via Akt1/SGK1-dependent phosphorylation of WNK1
- PMID: 21355052
- PMCID: PMC3060440
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010060681
Activation of PI3-kinase stimulates endocytosis of ROMK via Akt1/SGK1-dependent phosphorylation of WNK1
Abstract
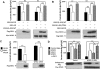
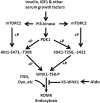
WNK kinases stimulate endocytosis of ROMK channels to regulate renal K+ handling. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-activating hormones, such as insulin and IGF 1, phosphorylate WNK1, but how this affects the regulation of ROMK abundance is unknown. Here, serum starvation of ROMK-transfected HEK cells led to an increase of ROMK current density; subsequent addition of insulin or IGF1 inhibited ROMK currents in a PI3K-dependent manner. Serum and insulin also increased phosphorylation of the downstream kinases Akt1 and SGK1 as well as WNK1. A biotinylation assay suggested that insulin and IGF1 inhibit ROMK by enhancing its endocytosis, a process that WNK1 may mediate. Knockdown of WNK1 with siRNA or expression of a phospho-deficient WNK1 mutant (T58A) both prevented insulin-induced inhibition of ROMK currents, suggesting that phosphorylation at Threonine-58 of WNK1 is important to mediate the inhibition of ROMK by PI3K-activating hormones or growth factors. In vitro and in vivo kinase assays supported the notion that Akt1 and SGK1 can phosphorylate WNK1 at this site, and we established that Akt1 and SGK1 synergistically inhibit ROMK through WNK1. We used dominant-negative intersectin and dynamin constructs to show that SGK1-mediated phosphorylation of WNK1 inhibits ROMK by promoting its endocytosis. Taken together, these results suggest that PI3K-activating hormones inhibit ROMK by enhancing its endocytosis via a mechanism that involves phosphorylation of WNK1 by Akt1 and SGK1.
Figures




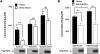

References
-
- Ho K, Nichols CG, Lederer WJ, Lytton J, Vassilev PM, Kanazirska MV, Hebert SC: Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature 362: 31–38, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Zeng WZ, Babich V, Ortega B, Quigley R, White SJ, Welling PA, Huang CL: Evidence for endocytosis of ROMK potassium channel via clathrin-coated vesicles. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283: F630–F639, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Xu B, English JM, Wilsbacher JL, Stippec S, Goldsmith EJ, Cobb MH: WNK1, a novel mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase lacking the catalytic lysine in subdomain II. J Biol Chem 275: 16795–16801, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Wilson FH, Disse-Nicode‘me S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP: Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 293: 1107–1112, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

