Risk for ESRD in type 1 diabetes remains high despite renoprotection
- PMID: 21355053
- PMCID: PMC3060448
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010040354
Risk for ESRD in type 1 diabetes remains high despite renoprotection
Abstract
Historically, patients with type 1 diabetes and macroalbuminuria had high competing risks: cardiovascular death or renal failure. Here, we assessed these risks in patients receiving therapies implemented during the last 30 years. Between 1991 and 2004, we enrolled 423 white patients with type 1 diabetes who developed macroalbuminuria (albumin excretion rate, ≥300 μg/min). With follow-up for 98% through 2008, ESRD developed in 172 patients (incidence rate, 5.8/100 person-years), and 29 died without ESRD (mortality rate, 1/100 person-years). The majority of these outcomes occurred between ages 36 and 52 years with durations of diabetes of 21 to 37 years. The 15-year cumulative risks were 52% for ESRD and 11% for pre-ESRD death. During the 15 years of follow-up, the use of renoprotective treatment increased from 56 to 82%, and BP and lipid levels improved significantly; however, the risks for both ESRD and pre-ESRD death did not change over the years analyzed. There were 70 post-ESRD deaths, and the mortality rate was very similar during the 1990s and the 2000s (11/100 person-years versus 12/100 person-years, respectively). Mortality was low in patients who received a pre-emptive kidney transplant (1/100 person-years), although these patients did not differ from dialyzed patients with regard to predialysis eGFR, sex, age at onset of ESRD, or duration of diabetes. In conclusion, despite the widespread adoption of renoprotective treatment, patients with type 1 diabetes and macroalbuminuria remain at high risk for ESRD, suggesting that more effective therapies are desperately needed.
Figures
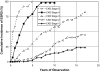
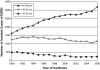
Comment in
-
Is treatment of nephropathy in type 1 diabetes efficacious but ineffective?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Mar;22(3):402-4. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011010076. Epub 2011 Feb 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21355059 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T: Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: An epidemiological study. Diabetologia 25: 496–501, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Krolewski AS, Warram JH, Christlieb AR, Busick EJ, Kahn CR: The changing natural history of nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Am J Med 78: 785–794, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Parving HH, Andersen AR, Smidt UM, Svendsen PA: Early aggressive antihypertensive treatment reduces rate of decline in kidney function in DN. Lancet 1: 1175–1179, 1983 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

