Intraoperative qRT-PCR for detection of lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer
- PMID: 21355082
- PMCID: PMC5270507
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3110
Intraoperative qRT-PCR for detection of lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Sentinel node biopsy (SNB) has been shown to accurately stage the regional lymphatics in oral carcinoma. However, intraoperative pathology is only moderately sensitive and final pathology takes several days to complete. The purpose of this study was to develop a rapid, automated, and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay that can match final pathology in an intraoperative time frame.
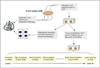
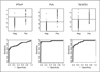
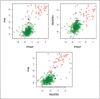
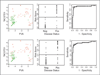
Experimental design: Four hundred forty-eight grossly tumor-negative lymph nodes were evaluated for expression of 3 markers [PVA (pemphigus vulgaris antigen), PTHrP (parathyroid hormone-related protein), and TACSTD1 (tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1)]. Conformity of metastasis detection by qRT-PCR was determined using hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemistry staining as the gold standard. PVA and TACSTD1 were then multiplexed with β-glucuronidase to develop a rapid, automated single-tube qRT-PCR assay using the Cepheid GeneXpert system. This assay was used to analyze 103 lymph nodes in an intraoperative time frame.
Results: Four hundred forty-two nodes produced an informative result for both qRT-PCR and pathologic examination. Concordance of qRT-PCR for individual markers with final pathology ranged from 93% to 98%. The best marker combination was TACSTD1 and PVA. A rapid, multiplex assay for TACSTD1 and PVA was developed on the Cepheid GeneXpert and demonstrated an excellent reproducibility and linearity. Analysis of 103 lymph nodes demonstrated 94.2% accuracy of this assay for identifying positive and negative nodes. The average time for each assay to yield results was 35 minutes.
Conclusions: A rapid, automated qRT-PCR assay can detect lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer with high accuracy compared to pathologic analysis and may be more accurate than intraoperative pathology. Combined, SNB and rapid qRT-PCR could more appropriately guide surgical treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
of Potential Conflicts of Interest No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Thekdi AA, Ferris RL. Diagnostic assessment of laryngeal cancer. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2002;35:953–969. - PubMed
-
- Takes RP. Staging of the neck in patients with head and neck squamous cell cancer: imaging techniques and biomarkers. Oral Oncol. 2004;40:656–667. - PubMed
-
- Shoaib T, Soutar DS, MacDonald DG, Camilleri IG, Dunaway DJ, Gray HW, et al. The accuracy of head and neck carcinoma sentinel lymph node biopsy in the clinically N0 neck. Cancer. 2001;91:2077–2083. - PubMed
-
- Kligerman J, Lima RA, Soares JR, Prado L, Dias FL, Freitas EQ, et al. Supraomohyoid neck dissection in the treatment of T1/T2 squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity. Am J Surg. 1994;168:391–394. - PubMed
-
- McGuirt WF, Jr, Johnson JT, Myers EN, Rothfield R, Wagner R. Floor of mouth carcinoma. The management of the clinically negative neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;121:278–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

