Non-coding RNAs enter mitosis: functions, conservation and implications
- PMID: 21356070
- PMCID: PMC3055801
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-6-6
Non-coding RNAs enter mitosis: functions, conservation and implications
Abstract
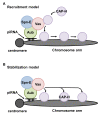
Nuage (or commonly known as chromatoid body in mammals) is a conserved germline-specific organelle that has been linked to the Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) pathway. piRNAs are a class of gonadal-specific RNAs that are ~23-29 nucleotides in length and protect genome stability by repressing the expression of deleterious retrotransposons. More recent studies in Drosophila have implicated the piRNA pathway in other functions including canalization of embryonic development, regulation of maternal gene expression and telomere protection. We have recently shown that Vasa (known as Mouse Vasa Homolog in mouse), a nuage component, plays a mitotic role in promoting chromosome condensation and segregation by facilitating robust chromosomal localization of condensin I in the Drosophila germline. Vasa functions together with Aubergine (a PIWI family protein) and Spindle-E/mouse TDRD-9, two other nuage components that are involved in the piRNA pathway, therefore providing a link between the piRNA pathway and mitotic chromosome condensation. Here, we propose and discuss possible models for the role of Vasa and the piRNA pathway during mitosis. We also highlight relevant studies implicating mitotic roles for RNAs and/or nuage in other model systems and their implications for cancer development.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

