Small RNA profiling of Dengue virus-mosquito interactions implicates the PIWI RNA pathway in anti-viral defense
- PMID: 21356105
- PMCID: PMC3060848
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-45
Small RNA profiling of Dengue virus-mosquito interactions implicates the PIWI RNA pathway in anti-viral defense
Abstract
Background: Small RNA (sRNA) regulatory pathways (SRRPs) are important to anti-viral defence in mosquitoes. To identify critical features of the virus infection process in Dengue serotype 2 (DENV2)-infected Ae. aegypti, we deep-sequenced small non-coding RNAs. Triplicate biological replicates were used so that rigorous statistical metrics could be applied.
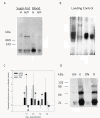
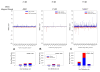
Results: In addition to virus-derived siRNAs (20-23 nts) previously reported for other arbovirus-infected mosquitoes, we show that PIWI pathway sRNAs (piRNAs) (24-30 nts) and unusually small RNAs (usRNAs) (13-19 nts) are produced in DENV-infected mosquitoes. We demonstrate that a major catalytic enzyme of the siRNA pathway, Argonaute 2 (Ago2), co-migrates with a ~1 megadalton complex in adults prior to bloodfeeding. sRNAs were cloned and sequenced from Ago2 immunoprecipitations. Viral sRNA patterns change over the course of infection. Host sRNAs were mapped to the published aedine transcriptome and subjected to analysis using edgeR (Bioconductor). We found that sRNA profiles are altered early in DENV2 infection, and mRNA targets from mitochondrial, transcription/translation, and transport functional categories are affected. Moreover, small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as tRNAs, spliceosomal U RNAs, and snoRNAs are highly enriched in DENV-infected samples at 2 and 4 dpi.
Conclusions: These data implicate the PIWI pathway in anti-viral defense. Changes to host sRNA profiles indicate that specific cellular processes are affected during DENV infection, such as mitochondrial function and ncRNA levels. Together, these data provide important progress in understanding the DENV2 infection process in Ae. aegypti.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

