Non-HDL-cholesterol as valid surrogate to apolipoprotein B100 measurement in diabetes: Discriminant Ratio and unbiased equivalence
- PMID: 21356116
- PMCID: PMC3056766
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-20
Non-HDL-cholesterol as valid surrogate to apolipoprotein B100 measurement in diabetes: Discriminant Ratio and unbiased equivalence
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB) is a superior indicator of CV risk than total or LDL-C. Non-HDL-C represents a simple surrogate for apoB in hypertriglyceridemic and/or T2DM patients. ApoB and non-HDL-C show high correlation, although the degree of mutual concordance remains debated in CV risk evaluation.
Objectives: We used the Discriminant Ratio (DR) methodology to compare the performance of non-HDL-C with that of apoB to rank diabetic patients according to dyslipidemia and to establish the underlying relationship between these variables taking measurement noise and intra-/intersubject variation into account, and to derive an unbiased equivalence equation.
Methods: Fasting total C, HDL-C, apoB and triglycerides were measured in 45 diabetic patients. The DR of the underlying between-subject standard deviation (SD) to the within-subject SD was calculated from duplicates. Correlation coefficients between pairs were adjusted to include an estimate of the underlying correlation.
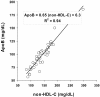
Results: Mean values [day 1 (1SD)] were 143 (36) mg/dl (non-HDL-C) and 98 (24) mg/dl (apoB). The DR's of both parameters were similar (1.76 and 1.83) (p = 0.83). Pearson's product-moment correlation coefficient between tests was very high (0.94), reaching unity (1.00) after attenuation adjustment. The unbiased equation of equivalence relating apoB to non-HDL-C had a slope of 0.65 and an intercept of 6.3 mg/dl.
Conclusions: The discrimination power of non-HDL-C is similar to that of apoB to rank diabetic patients according to atherogenic cholesterol and lipoprotein burden. Since true correlation between variables reached unity, non-HDL-C may provide not only a metabolic surrogate but also a candidate biometrical equivalent to apoB, as non-HDL-C calculation is readily available.
Figures
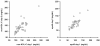
References
-
- Peter W Wilson, editor. Atlas of Atherosclerosis. Risk Factors and Treatment. Springer-Verlag New York; 2003. p. 284.
-
- Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–221. - PubMed
-
- Wägner AM, Pérez A, Zapico E, Ordóñez-Llanos J. Non-HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B in the dyslipidemic classification of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2048–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

