Intracellular signals mediating the food intake-suppressive effects of hindbrain glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation
- PMID: 21356521
- PMCID: PMC3108145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.001
Intracellular signals mediating the food intake-suppressive effects of hindbrain glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation
Erratum in
-
Intracellular Signals Mediating the Food Intake-Suppressive Effects of Hindbrain Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation.Cell Metab. 2016 Apr 12;23(4):745. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.02.010. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27076083 No abstract available.
Abstract
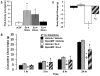
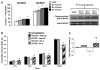
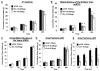
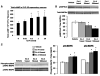
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) activation within the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) suppresses food intake and body weight (BW), but the intracellular signals mediating these effects are unknown. Here, hindbrain (fourth i.c.v.) GLP-1R activation by Exendin-4 (Ex-4) increased PKA and MAPK activity and decreased phosphorylation of AMPK in NTS. PKA and MAPK signaling contribute to food intake and BW suppression by Ex-4, as inhibitors RpcAMP and U0126 (fourth i.c.v.), respectively, attenuated Ex-4's effects. Hindbrain GLP-1R activation inhibited feeding by reducing meal number, not meal size. This effect was attenuated with stimulation of AMPK activity by AICAR (fourth i.c.v.). The PKA, MAPK, and AMPK signaling responses by Ex-4 were present in immortalized GLP-1R-expressing neurons (GT1-7). In conclusion, hindbrain GLP-1R activation suppresses food intake and BW through coordinated PKA-mediated suppression of AMPK and activation of MAPK. Pharmacotherapies targeting these signaling pathways, which mediate intake-suppressive effects of CNS GLP-1R activation, may prove efficacious in treating obesity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Chelikani PK, Haver AC, Reidelberger RD. Intravenous infusion of glucagon-like peptide-1 potently inhibits food intake, sham feeding, and gastric emptying in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288:R1695–1706. - PubMed
-
- Daniels D, Patten CS, Roth JD, Yee DK, Fluharty SJ. Melanocortin receptor signaling through mitogen-activated protein kinase in vitro and in rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 2003;986:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Daniels D, Yee DK, Faulconbridge LF, Fluharty SJ. Divergent behavioral roles of angiotensin receptor intracellular signaling cascades. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5552–5560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

