INX-08189, a phosphoramidate prodrug of 6-O-methyl-2'-C-methyl guanosine, is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication with excellent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties
- PMID: 21357300
- PMCID: PMC3088254
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01335-10
INX-08189, a phosphoramidate prodrug of 6-O-methyl-2'-C-methyl guanosine, is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication with excellent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties
Abstract
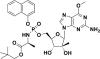
INX-08189 is an aryl-phosphoramidate of 6-O-methyl-2'-C-methyl guanosine. INX-08189 was highly potent in replicon assays, with a 50% effective concentration of 10±6 nM against hepatitis C genotype 1b at 72 h. The inhibitory effect on viral replication was rapid, with a 50% effective concentration (EC50) of 35±8 nM at 24 h. An intracellular 2'-C-methyl guanosine triphosphate (2'-C-MeGTP) concentration of 2.43±0.42 pmol/10(6) cells was sufficient to achieve 90% inhibition of viral replication. In vitro resistance studies confirmed that the S282T mutation in the NS5b gene conferred an approximately 10-fold reduction in sensitivity to INX-08189. However, the complete inhibition of S282T mutant replicons still could be achieved with an EC90 of 344±170 nM. Drug combination studies of INX-08189 and ribavirin indicated significant synergy in antiviral potency both in wild-type and S282T-expressing replicons. Genotype 1b replicons could be cleared after 14 days of culture when exposed to as little as 20 nM INX-08189. No evidence of mitochondrial toxicity was observed after 14 days of INX-08189 exposure in both HepG2 and CEM human cell lines. In vivo studies of rats and cynomolgus monkeys demonstrated that 2'-C-MeGTP concentrations in liver equivalent to the EC90 could be attained after a single oral dose of INX-08189. Rat liver 2'-C-MeGTP concentrations were proportional to dose, sustained for greater than 24 h, and correlated with plasma concentrations of the nucleoside metabolite 2'-C-methyl guanosine. The characteristics displayed by INX-08189 support its continued development as a clinical candidate for the treatment of chronic HCV infection.
Figures
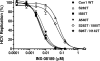
 ) NS5B sequences. Concentrations of INX-08189 are indicated on the x axis, and the measured luminescent signals are expressed as a percentage of signal obtained in no-treatment controls on the y axis. Symbols are means ± SD for triplicate determinations in a single experiment.
) NS5B sequences. Concentrations of INX-08189 are indicated on the x axis, and the measured luminescent signals are expressed as a percentage of signal obtained in no-treatment controls on the y axis. Symbols are means ± SD for triplicate determinations in a single experiment.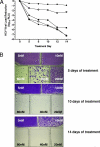
 ). Luciferase expression was monitored in the cultures at the indicated time points and expressed as log10 change in luminescence. (B) Cells were subcultured under G418 selection for up to 5 weeks, and surviving colonies were fixed and stained with crystal violet.
). Luciferase expression was monitored in the cultures at the indicated time points and expressed as log10 change in luminescence. (B) Cells were subcultured under G418 selection for up to 5 weeks, and surviving colonies were fixed and stained with crystal violet.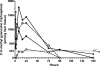
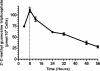
 ), 10 mg/kg (♢), 5 mg/kg (■), and 3 mg/kg (○). Symbols represent averages from two rats with the exception of the 3-mg/kg dose group, which included data from six rats. The EC90 determined for Huh-7 cells (243 pmol/g) is indicated by the dotted line.
), 10 mg/kg (♢), 5 mg/kg (■), and 3 mg/kg (○). Symbols represent averages from two rats with the exception of the 3-mg/kg dose group, which included data from six rats. The EC90 determined for Huh-7 cells (243 pmol/g) is indicated by the dotted line.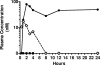
References
-
- Anderson P., Kakuda T. N., Lichtenstein K. A. 2004. The cellular pharmacology of nucleoside- and nucleotide-analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitors and its relationship to clinical toxicities. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:743–753 - PubMed
-
- Blight K. J., Kolykhalov A. A., Rice C. M. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972–1974 - PubMed
-
- Cahard D., McGuigan C., Balzarini J. 2004. Aryloxy phosphoramidate triesters as pro-tides. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 4:371–381 - PubMed
-
- Carroll S. S., Olsen D. B. 2006. Nucleoside analog inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication. Infect. Dis. Drug Targets 6:17–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

