Proteome dynamics and proteome function of cardiac 19S proteasomes
- PMID: 21357515
- PMCID: PMC3098593
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.006122
Proteome dynamics and proteome function of cardiac 19S proteasomes
Abstract
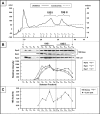
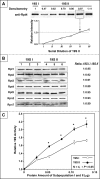
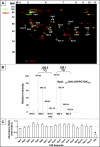
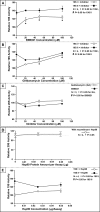
Myocardial proteasomes are comprised of 20S core particles and 19S regulatory particles, which together carry out targeted degradation of cardiac proteins. The 19S complex is unique among the regulators of proteasomes in that it affects both the capacity and specificity of protein degradation. However, a comprehensive molecular characterization of cardiac 19S complexes is lacking. In this investigation, we tailored a multidimensional chromatography-based purification strategy to isolate structurally intact and functionally viable 19S complexes from murine hearts. Two distinct subpopulations of 19S complexes were isolated based upon (1) potency of activating 20S proteolytic activity, and (2) molecular composition using a combination of immuno-detection, two-dimensional-differential gel electrophoresis, and MS-based approaches. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) was identified to be characteristic to 19S subpopulation I. The physical interaction of Hsp90 with 19S complexes was demonstrated via multiple approaches. Inhibition of Hsp90 activity using geldanamycin or BIIB021 potentiated the ability of subpopulation I to activate 20S proteasomes in the murine heart, thus demonstrating functional specificity of Hsp90 in subpopulation I. This investigation has advanced our understanding of the molecular heterogeneity of cardiac proteasomes by identifying molecularly and functionally distinct cardiac 19S complexes. The preferential association of Hsp90 with 19S subpopulation I unveils novel targets for designing proteasome-based therapeutic interventions for combating cardiac disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mapping the murine cardiac 26S proteasome complexes.Circ Res. 2006 Aug 18;99(4):362-71. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000237386.98506.f7. Epub 2006 Jul 20. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16857966
-
Regulation of murine cardiac 20S proteasomes: role of associating partners.Circ Res. 2006 Aug 18;99(4):372-80. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000237389.40000.02. Epub 2006 Jul 20. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16857963
-
Contrasting proteome biology and functional heterogeneity of the 20 S proteasome complexes in mammalian tissues.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Feb;8(2):302-15. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800058-MCP200. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 18931337 Free PMC article.
-
The murine cardiac 26S proteasome: an organelle awaiting exploration.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1047:197-207. doi: 10.1196/annals.1341.018. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16093497 Review.
-
Comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of the 20S proteasome complex.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:187-236. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05009-3. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413316 Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into Bortezomib Focusing on Its Efficacy against P-gp-Positive MDR Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 23;22(11):5504. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115504. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071136 Free PMC article.
-
Novel epigenetic-based therapies useful in cardiovascular medicine.World J Cardiol. 2016 Feb 26;8(2):211-9. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i2.211. World J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26981216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin proteasome system and myocardial ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Feb 1;304(3):H337-49. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00604.2012. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23220331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slow-twitch skeletal muscle defects accompany cardiac dysfunction in transgenic mice with a mutation in the myosin regulatory light chain.FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3152-3166. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801402R. Epub 2018 Oct 26. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30365366 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modification of cardiac proteasomes: functional delineation enabled by proteomics.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jul;303(1):H9-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00189.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22523251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patterson C., Ike C., Willis P. W., 4th, Stouffer G. A., Willis M. S. (2007) The bitter end: the ubiquitin-proteasome system and cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 115, 1456–1463 - PubMed
-
- Gomes A. V., Zong C., Edmondson R. D., Berhane B. T., Wang G. W., Le S., Young G., Zhang J., Vondriska T. M., Whitelegge J. P., Jones R. C., Joshua I. G., Thyparambil S., Pantaleon D., Qiao J., Loo J., Ping P. (2005) The murine cardiac 26S proteasome: an organelle awaiting exploration. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1047, 197–207 - PubMed
-
- Bulteau A. L., Szweda L. I., Friguet B. (2002) Age-dependent declines in proteasome activity in the heart. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 397, 298–304 - PubMed
-
- Bulteau A. L., Lundberg K. C., Humphries K. M., Sadek H. A., Szweda P. A., Friguet B., Szweda L. I. (2001) Oxidative modification and inactivation of the proteasome during coronary occlusion/reperfusion. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 30057–30063 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

