Chaperone activity of α B-crystallin is responsible for its incorrect assignment as an autoantigen in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 21357544
- PMCID: PMC3741407
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003934
Chaperone activity of α B-crystallin is responsible for its incorrect assignment as an autoantigen in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
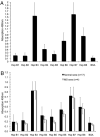
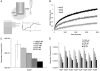
For 15 y, α B-crystallin (heat shock protein [Hsp] B5) has been labeled an autoantigen in multiple sclerosis (MS) based on humoral and cellular responses found in humans and animal models. However, there have been several scientific inconsistencies with this assignment, ranging from studies demonstrating small differences in anticrystallin responses between patients and healthy individuals to the inability of crystallin-specific T cells to induce symptoms of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in animal models. Experiments in this article demonstrate that the putative anti-HspB5 Abs from 23 MS patients cross-react with 7 other members of the human small Hsp family and were equally present in normal plasma. Biolayer interferometry demonstrates that the binding was temperature dependent, and that the calculated K(a) increased as the concentration of the sHsp decreased. These two patterns are characteristic of multiple binding sites with varying affinities, the composition of which changes with temperature, supporting the hypothesis that HspB5 bound the Ab and not the reverse. HspB5 also precipitated Ig heavy and L chains from sera from patients with MS. These results establish that small Hsps bind Igs with high affinity and refute much of the serological data used to assign α B-crystallin as an autoantigen.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Chaperone activity of α B-crystallin is responsible for its incorrect assignment as an autoantigen in multiple sclerosis".J Immunol. 2011 Jul 1;187(1):3; author reply 3-4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1190025. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21690329 No abstract available.
References
-
- Steinman L. A molecular trio in relapse and remission in multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:440–447. - PubMed
-
- van Noort JM, van Sechel AC, Bajramovic JJ, el Ouagmiri M, Polman CH, Lassmann H, Ravid R. The small heat-shock protein alpha B-crystallin as candidate autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1995;375:798–801. - PubMed
-
- van Noort JM, Verbeek R, Meilof JF, Polman CH, Amor S. Autoantibodies against alpha B-crystallin, a candidate autoantigen in multiple sclerosis, are part of a normal human immune repertoire. Mult Scler. 2006;12:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Celet B, Akman-Demir G, Serdaroğlu P, Yentür SP, Taşci B, van Noort JM, Eraksoy M, Saruhan-Direskeneli G. Anti-alpha B-crystallin immunoreactivity in inflammatory nervous system diseases. J Neurol. 2000;247:935–939. - PubMed
-
- Joachim SC, Bruns K, Lackner KJ, Pfeiffer N, Grus FH. Antibodies to alpha B-crystallin, vimentin, and heat shock protein 70 in aqueous humor of patients with normal tension glaucoma and IgG antibody patterns against retinal antigen in aqueous humor. Curr Eye Res. 2007;32:501–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

