Epigallocatechin-3-gallate potently inhibits the in vitro activity of hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase
- PMID: 21357570
- PMCID: PMC3073461
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M011817
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate potently inhibits the in vitro activity of hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase
Abstract
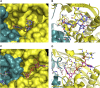
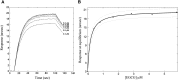
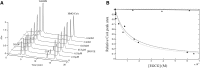
Hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR) is the rate-controlling enzyme of cholesterol synthesis, and owing to its biological and pharmacological relevance, researchers have investigated several compounds capable of modulating its activity with the hope of developing new hypocholesterolemic drugs. In particular, polyphenol-rich extracts were extensively tested for their cholesterol-lowering effect as alternatives, or adjuvants, to the conventional statin therapies, but a full understanding of the mechanism of their action has yet to be reached. Our work reports on a detailed kinetic and equilibrium study on the modulation of HMGR by the most-abundant catechin in green tea, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Using a concerted approach involving spectrophotometric, optical biosensor, and chromatographic analyses, molecular docking, and site-directed mutagenesis on the cofactor site of HMGR, we have demonstrated that EGCG potently inhibits the in vitro activity of HMGR (K(i) in the nanomolar range) by competitively binding to the cofactor site of the reductase. Finally, we evaluated the effect of combined EGCG-statin administration.
Figures



References
-
- Berry J. D., Liu K., Folsom A. R., Lewis C. E., Carr J. J., Polak J. F., Shea S., Sidney S., O'Leary D. H., Chan C., et al. 2009. Prevalence and progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in younger adults with low short-term but high lifetime estimated risk for cardiovascular disease: the coronary artery risk development in young adults study and multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circulation. 119: 382–389. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Steinberger J., Daniels S. R., Eckel R. H., Hayman L., Lustig R. H., McCrindle B., Mietus-Snyder M. L. 2009. Progress and challenges in metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 119: 628–647. - PubMed
-
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. 1980. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J. Lipid Res. 21: 505–517. - PubMed
-
- Edwards P. A., Lemongello D., Kane J., Shechter I., Fogelman A. M. 1980. Properties of purified rat hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and regulation of enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 255: 3715–3725. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

