Results of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group D9602 protocol, using vincristine and dactinomycin with or without cyclophosphamide and radiation therapy, for newly diagnosed patients with low-risk embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children's Oncology Group
- PMID: 21357783
- PMCID: PMC3083999
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.4469
Results of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group D9602 protocol, using vincristine and dactinomycin with or without cyclophosphamide and radiation therapy, for newly diagnosed patients with low-risk embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children's Oncology Group
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with localized, grossly resected, or gross residual (orbital only) embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) had 5-year failure-free survival (FFS) rates of 83% and overall survival rates of 95% on Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG) protocols III/IV. IRSG D9602 protocol (1997 to 2004) objectives were to decrease toxicity in similar patients by reducing radiotherapy (RT) doses and eliminating cyclophosphamide for the lowest-risk patients.
Patients and methods: Subgroup A patients (lowest risk, with ERMS, stage 1 group I/IIA, stage 1 group III orbit, stage 2 group I) received vincristine plus dactinomycin (VA). Subgroup B patients (ERMS, stage 1 group IIB/C, stage I group III nonorbit, stage 2 group II, stage 3 group I/II) received VA plus cyclophosphamide. Patients in group II/III received RT. Compared with IRS-IV, doses were reduced from 41.4 to 36 Gy for stage 1 group IIA patients and from 50 or 59 to 45 Gy for group III orbit patients.
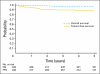
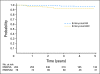
Results: Estimated 5-year FFS rates were 89% (95% CI, 84% to 92%) for subgroup A patients (n = 264) and 85% (95% CI, 74%, 91%) for subgroup B patients (n = 78); median follow-up: 5.1 years. Estimated 5-year FFS rates were 81% (95% CI, 68% to 90%) for patients with stage 1 group IIA tumors (n = 62) and 86% (95% CI, 76% to 92%) for patients with group III orbit tumors (n = 77).
Conclusion: Five-year FFS and OS rates were similar to those observed in comparable IRS-III patients, including patients receiving reduced RT doses, but were lower than in comparable IRS-IV patients receiving VA plus cyclophosphamide. Five-year FFS rates were similar among subgroups A and B patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Maurer HM, Beltangady M, Gehan EA, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-I: A final report. Cancer. 1988;61:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Maurer HM, Gehan EA, Beltangady M, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-II. Cancer. 1993;71:1904–1922. - PubMed
-
- Crist W, Gehan EA, Ragab AH, et al. The Third Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:610–630. - PubMed
-
- Crist WM, Anderson JR, Meza JL, et al. Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-IV: Results for patients with nonmetastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3091–3102. - PubMed
-
- Mandell L, Ghavimi F, Peretz T, et al. Radiocurability of microscopic disease in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma with radiation doses less than 4000 cGy. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:1536–1542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

