Protein kinase D signaling: multiple biological functions in health and disease
- PMID: 21357900
- PMCID: PMC4381749
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00037.2010
Protein kinase D signaling: multiple biological functions in health and disease
Abstract
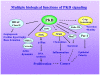
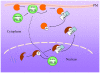
Protein kinase D (PKD) is an evolutionarily conserved protein kinase family with structural, enzymological, and regulatory properties different from the PKC family members. Signaling through PKD is induced by a remarkable number of stimuli, including G-protein-coupled receptor agonists and polypeptide growth factors. PKD1, the most studied member of the family, is increasingly implicated in the regulation of a complex array of fundamental biological processes, including signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation, membrane trafficking, secretion, immune regulation, cardiac hypertrophy and contraction, angiogenesis, and cancer. PKD mediates such a diverse array of normal and abnormal biological functions via dynamic changes in its spatial and temporal localization, combined with its distinct substrate specificity. Studies on PKD thus far indicate a striking diversity of both its signal generation and distribution and its potential for complex regulatory interactions with multiple downstream pathways, often regulating the subcellular localization of its targets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D: a new player among the signaling proteins that regulate functions in the nervous system.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Jun;30(3):497-504. doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1403-2. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 24526660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase D signaling in cancer: A friend or foe?Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Aug;1868(1):283-294. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.05.008. Epub 2017 May 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28577984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKD at the crossroads of DAG and PKC signaling.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Jun;27(6):317-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2006.04.003. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16678913 Review.
-
A Novel Conserved Domain Mediates Dimerization of Protein Kinase D (PKD) Isoforms: DIMERIZATION IS ESSENTIAL FOR PKD-DEPENDENT REGULATION OF SECRETION AND INNATE IMMUNITY.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23516-23531. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.735399. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27662904 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal peptide signalling in health and disease.Eur J Surg Suppl. 2002;(587):23-38. Eur J Surg Suppl. 2002. PMID: 16144198 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for phospholipase D in angiotensin II-induced protein kinase D activation in adrenal glomerulosa cell models.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Feb 5;366(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23178798 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase Cε hydrolyzes perinuclear phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate to regulate cardiac hypertrophy.Cell. 2013 Mar 28;153(1):216-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.047. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23540699 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and protein kinase D1 related pathways by a multiple kinase inhibitor in angiogenesis and inflammation related processes in vitro.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 14;10(4):e0124234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124234. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25874616 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing growth regulatory roles of protein kinase D isoforms in human keratinocytes.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 24;290(17):11199-208. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.643742. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25802335 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreas-specific deletion of protein kinase D attenuates inflammation, necrosis, and severity of acute pancreatitis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Jan 1;1867(1):165987. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165987. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33039594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avkiran M, Rowland AJ, Cuello F, Haworth RS. Protein kinase d in the cardiovascular system: emerging roles in health and disease. Circ Res. 2008;102:157–163. - PubMed
-
- Azoitei N, Pusapati GV, Kleger A, MÃüller P, Köfer R, Genze F, Wagner M, van Lint J, Carmeliet P, Adler G, Seufferlein T. Protein kinase D2 is a crucial regulator of tumour cellǎ£“endothelial cell communication in gastrointestinal tumours. Gut. 2010;59:1316. - PubMed
-
- Bardswell SC, Cuello F, Rowland AJ, Sadayappan S, Robbins J, Gautel M, Walker JW, Kentish JC, Avkiran M. Distinct Sarcomeric Substrates Are Responsible for Protein Kinase D-mediated Regulation of Cardiac Myofilament Ca2+ Sensitivity and Cross-bridge Cycling. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:5674–5682. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

