Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43
- PMID: 21358640
- PMCID: PMC3108889
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2778
Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43
Abstract
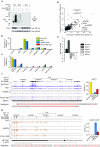
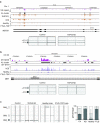
TDP-43 is a predominantly nuclear RNA-binding protein that forms inclusion bodies in frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The mRNA targets of TDP-43 in the human brain and its role in RNA processing are largely unknown. Using individual nucleotide-resolution ultraviolet cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (iCLIP), we found that TDP-43 preferentially bound long clusters of UG-rich sequences in vivo. Analysis of RNA binding by TDP-43 in brains from subjects with FTLD revealed that the greatest increases in binding were to the MALAT1 and NEAT1 noncoding RNAs. We also found that binding of TDP-43 to pre-mRNAs influenced alternative splicing in a similar position-dependent manner to Nova proteins. In addition, we identified unusually long clusters of TDP-43 binding at deep intronic positions downstream of silenced exons. A substantial proportion of alternative mRNA isoforms regulated by TDP-43 encode proteins that regulate neuronal development or have been implicated in neurological diseases, highlighting the importance of TDP-43 for the regulation of splicing in the brain.
Figures


Comment in
-
TDP-43: multiple targets, multiple disease mechanisms?Nat Neurosci. 2011 Apr;14(4):403-5. doi: 10.1038/nn.2784. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21445063 No abstract available.
-
Neurodegenerative disease: a target map for TDP43.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 May;12(5):246. doi: 10.1038/nrn3032. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21505508 No abstract available.
References
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE. Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front Biosci. 2008;13:867–878. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36337–36343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

