Elimination of neglected diseases in latin america and the Caribbean: a mapping of selected diseases
- PMID: 21358810
- PMCID: PMC3039687
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000964
Elimination of neglected diseases in latin america and the Caribbean: a mapping of selected diseases
Abstract
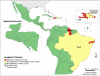
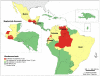
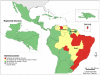
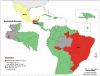
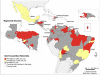
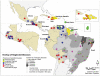
In Latin America and the Caribbean, around 195 million people live in poverty, a situation that increases the burden of some infectious diseases. Neglected diseases, in particular, are often restricted to poor, marginalized sections of the population. Tools exist to combat these diseases, making it imperative to work towards their elimination. In 2009, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) received a mandate to support the countries in the Region in eliminating neglected diseases and other poverty-related infections. The objective of this study is to analyze the presence of selected diseases using geo-processing techniques. Five diseases with information available at the first sub-national level (states) were mapped, showing the presence of the disease ("hotspots") and overlap of diseases ("major hotspots"). In the 45 countries/territories (approximately 570 states) of the Region, there is: lymphatic filariasis in four countries (29 states), onchocerciasis in six countries (25 states), schistosomiasis in four countries (39 states), trachoma in three countries (29 states), and human rabies transmitted by dogs in ten countries (20 states). Of the 108 states with one or more of the selected diseases, 36 states present the diseases in overlapping areas ("major hotspots"). Additional information about soil-transmitted helminths was included. The analysis suggests a majority of the selected diseases are not widespread and can be considered part of an unfinished agenda with elimination as a goal. Integrated plans and a comprehensive approach, ensuring access to existing diagnostic and treatment methods, and establishing a multi-sectoral agenda that addresses social determinants, including access to adequate water and sanitation, are required. Future studies can include additional diseases, socio-economic and environmental variables.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Comisión Económica para America Latina y el Cartbe. Vol. 9. Santiago: CEPAL; 2007. Panorama social de America Latina 2007. Available: http://www.eclac.org/cgi-bin/getProd.asp?xml=/publicaciones/xml/5/30305/.... Accessed 2009 Sep.
-
- World Health Organization. Geneva: WHO; 2007. Global Plan to Combat Neglected Tropical Diseases 2008–2015. (WHO/CDS/NTD/2007.3)
-
- Holveck J, Ehrenberg J, Ault S, Rojas R, Vasquez J, et al. Prevention, control and elimination of neglected diseases in the Americas: Pathways to integrated, inter-programmatic, intersectoral action for health and development. BMC Public Health 7. 2007 Available: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/7/6/. Accessed 2009 Jun 10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pruss A, Bos R, Gore F, Bartram J. Geneva: WHO; 2008. Safer water, better health: costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health. Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241596435_eng.pdf. Accessed 2009 Jun 12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

