Rituximab therapy reduces organ-specific T cell responses and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 21359213
- PMCID: PMC3040191
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017103
Rituximab therapy reduces organ-specific T cell responses and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
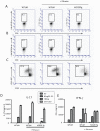
Recent clinical trials have established B cell depletion by the anti-CD20 chimeric antibody Rituximab as a beneficial therapy for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS). The impact of Rituximab on T cell responses remains largely unexplored. In the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS in mice that express human CD20, Rituximab administration rapidly depleted peripheral B cells and strongly reduced EAE severity. B cell depletion was also associated with diminished Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) and a reduction in T cell proliferation and IL-17 production during recall immune response experiments. While Rituximab is not considered a broad immunosuppressant, our results indicate a role for B cells as a therapeutic cellular target in regulating encephalitogenic T cell responses in specific tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bauman TM, Kasper LH. Novel approaches and cutting edge immunotherapies in multiple sclerosis. Front Biosci. 2004;9:2302–2322. - PubMed
-
- Menge T, Weber MS, Hemmer B, Kieseier BC, von Budingen HC, et al. Disease-modifying agents for multiple sclerosis: recent advances and future prospects. Drugs. 2008;68:2445–2468. - PubMed
-
- Grillo-Lopez AJ, Hedrick E, Rashford M, Benyunes M. Rituximab: ongoing and future clinical developmemt. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Stuve O, Cepok S, Elias B, Saleh A, Hartung HP, Hemmer B, et al. Arch Neurol In Press; 2005. Clinical Stabilization and Effective B cell Depletion in the Cerebrospinal Fluid and Peripheral Blood in a Patient with Fulminant Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. - PubMed
-
- Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, Vollmer T, Antel J, et al. B-cell depletion with Rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:676–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

