Outcomes of adult living donor liver transplantation: comparison of the Adult-to-adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Cohort Study and the national experience
- PMID: 21360649
- PMCID: PMC3116058
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.22288
Outcomes of adult living donor liver transplantation: comparison of the Adult-to-adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Cohort Study and the national experience
Abstract
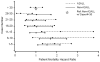
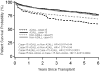
The study objectives were to determine whether the findings of the Adult-to-Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Cohort Study (A2ALL) reflect the U.S. national experience and to define risk factors for patient mortality and graft loss in living donor liver transplantation (LDLT). A2ALL previously identified risk factors for mortality after LDLT, which included early center experience, older recipient age, and longer cold ischemia time. LDLT procedures at 9 A2ALL centers (n = 702) and 67 non-A2ALL centers (n = 1664) from January 1998 through December 2007 in the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients database were analyzed. Potential predictors of time from transplantation to death or graft failure were tested using Cox regression. No significant difference in overall mortality between A2ALL and non-A2ALL centers was found. Higher hazard ratios (HRs) were associated with donor age (HR = 1.13 per 10 years, P = 0.0002), recipient age (HR = 1.20 per 10 years, P = 0.0003), serum creatinine levels (HR = 1.52 per loge unit increase, P < 0.0001), hepatocellular carcinoma (HR = 2.12, P<0.0001) or hepatitis C virus (HR = 1.18, P = 0.026), intensive care unit stay (HR = 2.52, P< 0.0001) or hospitalization (HR = 1.62, P < 0.0001) versus home, earlier center experience (LDLT case number 15: HR = 1.61, P < 0.0001, and a cold ischemia time >4.5 hours (HR = 1.79, P = 0.0006). Except for center experience, risk factor effects between A2ALL and non-A2ALL centers were not significantly different. Variables associated with graft loss were identified and showed similar trends. In conclusion, mortality and graft loss risk factors were similar in A2ALL and non-A2ALL centers. These analyses demonstrate that findings from the A2ALL consortium are relevant to other centers in the U.S. performing LDLT, and conclusions and recommendations from A2ALL may help to guide clinical decision making.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures





References
-
- Wachs ME, Bak TE, Karrer FM, Everson GT, Shrestha R, Trouillot TE, Mandell MS, et al. Adult living donor liver transplantation using a right hepatic lobe. Transplantation. 1998;66:1313–1316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK062496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062484/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62484/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK62496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
