Control of the stability of a protein-RNA complex by the position of fluorine in a base analogue
- PMID: 21361282
- PMCID: PMC3095225
- DOI: 10.1021/ja102601h
Control of the stability of a protein-RNA complex by the position of fluorine in a base analogue
Erratum in
- J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Sep 3;136(35):12514
Abstract
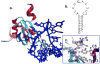
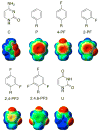
The effects of modifying the electronic characteristics of nonpolar base analogues substituted at positions involved in stacking interactions between SL2 RNA and the U1A protein are described. A surprisingly large difference in the stability between complexes formed with base analogues that differ only in the position of substitution of a single fluorine atom is observed. The results of high-level ab initio calculations of the interactions between the nonpolar base analogue and the amino acid side chain correlate with the experimentally observed trends in complex stability, which suggests that changes in stacking interactions that result from varying the position and degree of fluorine substitution contribute to the effects of fluorine substitution on the stability of the U1A-SL2 RNA complex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of a conserved stacking interaction in target site recognition by the U1A protein.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 15;30(2):550-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.2.550. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11788718 Free PMC article.
-
Two structurally different RNA molecules are bound by the spliceosomal protein U1A using the same recognition strategy.Structure. 1996 May 15;4(5):621-31. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00066-4. Structure. 1996. PMID: 8736559
-
Stacking interactions in PUF-RNA complexes.RNA. 2011 Apr;17(4):718-27. doi: 10.1261/rna.2540311. Epub 2011 Mar 3. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21372189 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in RNA-protein recognition.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Feb;11(1):53-8. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00164-0. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11179892 Review.
-
Modulating the Efficacy of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors through Fluorine Substitution.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Oct 18;60(43):23068-23082. doi: 10.1002/anie.202103211. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 34028153 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorine bonding enhances the energetics of protein-lipid binding in the gas phase.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 May;25(5):751-7. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0837-8. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24658801
-
Rational redesign of a cation···π···π stacking at cardiovascular Fbw7-Skp1 complex interface and its application for deriving self-inhibitory peptides to disrupt the complex interaction.J Mol Model. 2017 Sep 26;23(10):296. doi: 10.1007/s00894-017-3456-z. J Mol Model. 2017. PMID: 28952040
References
-
- Cozzi F, Ponzini F, Annunziata R, Cinquini M, Siegel JS. Angew Chem. 1995;34:1019.
- Collins SK, El-Azizi Y, Schmitzer AR. J Org Chem. 2007;72:6397. - PubMed
- Zakarian JE, El-Azizi Y, Collins SK. Org Lett. 2008;10:2927. - PubMed
- Cockroft SL, Hunter CA, Lawson KR, Perkins J, Urch CJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:8594. - PubMed
- Shu L, Müri M, Krupkea R, Mayor M. Org Biomol Chem. 2009;7:1081–1092. - PubMed
-
- Kopitz H, Zivkovic A, Engels JW, Gohlke H. Chem Bio Chem. 2008;9:2619. - PubMed
- Waters ML. Biopolymers. 2004;76:435. - PubMed
- Zahn A, Brotschi C, Leumann CJ. Chem Eur J. 2005;11:2125. - PubMed
- Mathis G, Hunziker J. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2002;41:3203. - PubMed
- Gorske BC, Blackwell HE. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:14378. - PubMed
-
- Cléry A, Blatter M, Allain FHT. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:290. - PubMed
- Green MR. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559. - PubMed
- Boelens WC, Jansen EJR, van Venrooij WJ, Stripecke R, Mattaj IW, Gunderson SI. Cell. 1993;72:881. - PubMed
- Liang S, Lutz CS. RNA. 2006;12:111. - PMC - PubMed
- Phillips C, Pachikara N, Gunderson SI. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:6162. - PMC - PubMed
- Oubridge C, Ito N, Evans PR, Teo CH, Nagai K. Nature. 1994;372:432. - PubMed
- Kranz JK, Lu J, Hall KB. Protein Sci. 1996;5:1567. - PMC - PubMed
- Showalter SA, Hall KB. J Mol Biol. 2004;335:465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

