Reduced fidelity of branch point recognition and alternative splicing induced by the anti-tumor drug spliceostatin A
- PMID: 21363963
- PMCID: PMC3049286
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2014311
Reduced fidelity of branch point recognition and alternative splicing induced by the anti-tumor drug spliceostatin A
Abstract
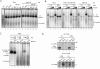
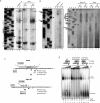
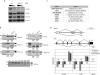
Spliceostatin A (SSA) is a stabilized derivative of a Pseudomonas bacterial fermentation product that displays potent anti-proliferative and anti-tumor activities in cancer cells and animal models. The drug inhibits pre-mRNA splicing in vitro and in vivo and binds SF3b, a protein subcomplex of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), which is essential for recognition of the pre-mRNA branch point. We report that SSA prevents interaction of an SF3b 155-kDa subunit with the pre-mRNA, concomitant with nonproductive recruitment of U2 snRNP to sequences 5' of the branch point. Differences in base-pairing potential with U2 snRNA in this region lead to different sensitivity of 3' splice sites to SSA, and to SSA-induced changes in alternative splicing. Indeed, rather than general splicing inhibition, splicing-sensitive microarray analyses reveal specific alternative splicing changes induced by the drug that significantly overlap with those induced by knockdown of SF3b 155. These changes lead to down-regulation of genes important for cell division, including cyclin A2 and Aurora A kinase, thus providing an explanation for the anti-proliferative effects of SSA. Our results reveal a mechanism that prevents nonproductive base-pairing interactions in the spliceosome, and highlight the regulatory and cancer therapeutic potential of perturbing the fidelity of splice site recognition.
Figures

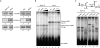

References
-
- Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ 2010. Deciphering the splicing code. Nature 465: 53–59 - PubMed
-
- Bennett M, Reed R 1993. Correspondence between a mammalian spliceosome component and an essential yeast splicing factor. Science 262: 105–108 - PubMed
-
- Berglund JA, Chua K, Abovich N, Reed R, Rosbash M 1997. The splicing factor BBP interacts specifically with the pre-mRNA branchpoint sequence UACUAAC. Cell 89: 781–787 - PubMed
-
- Bonnal S, Martinez C, Forch P, Bachi A, Wilm M, Valcarcel J 2008. RBM5/Luca-15/H37 regulates Fas alternative splice site pairing after exon definition. Mol Cell 32: 81–95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
