High-throughput phenotyping using parallel sequencing of RNA interference targets in the African trypanosome
- PMID: 21363968
- PMCID: PMC3106324
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.115089.110
High-throughput phenotyping using parallel sequencing of RNA interference targets in the African trypanosome
Abstract
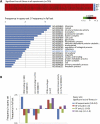
African trypanosomes are major pathogens of humans and livestock and represent a model for studies of unusual protozoal biology. We describe a high-throughput phenotyping approach termed RNA interference (RNAi) target sequencing, or RIT-seq that, using Illumina sequencing, maps fitness-costs associated with RNAi. We scored the abundance of >90,000 integrated RNAi targets recovered from trypanosome libraries before and after induction of RNAi. Data are presented for 7435 protein coding sequences, >99% of a non-redundant set in the Trypanosoma brucei genome. Analysis of bloodstream and insect life-cycle stages and differentiated libraries revealed genome-scale knockdown profiles of growth and development, linking thousands of previously uncharacterized and "hypothetical" genes to essential functions. Genes underlying prominent features of trypanosome biology are highlighted, including the constitutive emphasis on post-transcriptional gene expression control, the importance of flagellar motility and glycolysis in the bloodstream, and of carboxylic acid metabolism and phosphorylation during differentiation from the bloodstream to the insect stage. The current data set also provides much needed genetic validation to identify new drug targets. RIT-seq represents a versatile new tool for genome-scale functional analyses and for the exploitation of genome sequence data.
Figures






Comment in
-
Understanding sleeping sickness.Nat Methods. 2011 May;8(5):370-1. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0511-370b. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21678618 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alibu VP, Storm L, Haile S, Clayton C, Horn D 2005. A doubly inducible system for RNA interference and rapid RNAi plasmid construction in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol 139: 75–82 - PubMed
-
- Berriman M, Ghedin E, Hertz-Fowler C, Blandin G, Renauld H, Bartholomeu DC, Lennard NJ, Caler E, Hamlin NE, Haas B, et al. 2005. The genome of the African trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei. Science 309: 416–422 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
