Rapid, reversible activation of AgRP neurons drives feeding behavior in mice
- PMID: 21364278
- PMCID: PMC3069789
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI46229
Rapid, reversible activation of AgRP neurons drives feeding behavior in mice
Abstract
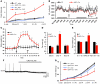
Several different neuronal populations are involved in regulating energy homeostasis. Among these, agouti-related protein (AgRP) neurons are thought to promote feeding and weight gain; however, the evidence supporting this view is incomplete. Using designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADD) technology to provide specific and reversible regulation of neuronal activity in mice, we have demonstrated that acute activation of AgRP neurons rapidly and dramatically induces feeding, reduces energy expenditure, and ultimately increases fat stores. All these effects returned to baseline after stimulation was withdrawn. In contrast, inhibiting AgRP neuronal activity in hungry mice reduced food intake. Together, these findings demonstrate that AgRP neuron activity is both necessary and sufficient for feeding. Of interest, activating AgRP neurons potently increased motivation for feeding and also drove intense food-seeking behavior, demonstrating that AgRP neurons engage brain sites controlling multiple levels of feeding behavior. Due to its ease of use and suitability for both acute and chronic regulation, DREADD technology is ideally suited for investigating the neural circuits hypothesized to regulate energy balance.
Figures

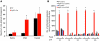
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS064882/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM008719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA017204/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH087074/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37DK053477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH61887/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH087074/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH082441/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK053477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32DK089710-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19MH82441/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA017204/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA027120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK089710/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK071051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK069983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061887/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

