E3 ubiquitin ligases and abscisic acid signaling
- PMID: 21364320
- PMCID: PMC3142413
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.3.13914
E3 ubiquitin ligases and abscisic acid signaling
Abstract
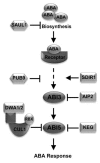
The ubiquitin proteasome system is involved in the regulation of nearly every aspect of plant growth and development. Protein ubiquitination involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to target proteins through a cascade catalyzed by three enzymes known as E1, E2 and E3. E3s, which are of particular interest as they confer substrate specificity during ubiquitination through their diverse substrate recognition domains. Recently, a number of E3s have been identified that actively participate in abscisic acid hormone biology, including regulation of biosynthesis, de-repression or activation of abscisic acid response and degradation of signaling components. In this review, we summarize recent exciting studies of the different type of E3s that target specific mediators of abscisic acid signaling or affect the plants response to the hormone.
Figures
References
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Smalle J, Vierstra RD. The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004;55:555–590. - PubMed
-
- Stone SL, Callis J. Ubiquitin ligases mediate growth and development by promoting protein death. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007;10:624–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
