Long-term (trophic) purinergic signalling: purinoceptors control cell proliferation, differentiation and death
- PMID: 21364628
- PMCID: PMC3032501
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2009.11
Long-term (trophic) purinergic signalling: purinoceptors control cell proliferation, differentiation and death
Abstract
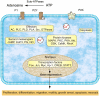
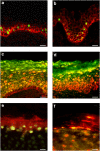
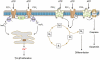
The purinergic signalling system, which uses purines and pyrimidines as chemical transmitters, and purinoceptors as effectors, is deeply rooted in evolution and development and is a pivotal factor in cell communication. The ATP and its derivatives function as a 'danger signal' in the most primitive forms of life. Purinoceptors are extraordinarily widely distributed in all cell types and tissues and they are involved in the regulation of an even more extraordinary number of biological processes. In addition to fast purinergic signalling in neurotransmission, neuromodulation and secretion, there is long-term (trophic) purinergic signalling involving cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and death in the development and regeneration of most systems of the body. In this article, we focus on the latter in the immune/defence system, in stratified epithelia in visceral organs and skin, embryological development, bone formation and resorption, as well as in cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Lohmann K. Uber die Pyrophosphatfraktion im Muskel. Naturwissenschaften. 1929;17:624–625.
-
- Fiske CH, SubbaRow Y. Phosphorous compounds of muscle and liver. Science. 1929;70:381–382. - PubMed
-
- Lippman F. Metabolic generation and utilization of phosphate bond energy. Enzymology. 1941;1:99.
-
- Ponnamperuma C, Sagan C, Mariner R. Synthesis of adenosine triphosphate under possible primitive earth conditions. Nature. 1963;199:222–226. - PubMed
-
- Waldrop MM. Did life really start out in an RNA world. Science. 1989;246:1248–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

