Protective effector memory CD4 T cells depend on ICOS for survival
- PMID: 21364749
- PMCID: PMC3041765
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016529
Protective effector memory CD4 T cells depend on ICOS for survival
Abstract
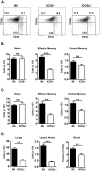
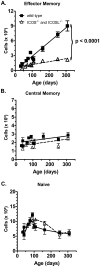
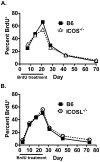
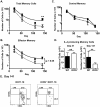
Memory CD4 T cells play a vital role in protection against re-infection by pathogens as diverse as helminthes or influenza viruses. Inducible costimulator (ICOS) is highly expressed on memory CD4 T cells and has been shown to augment proliferation and survival of activated CD4 T cells. However, the role of ICOS costimulation on the development and maintenance of memory CD4 T cells remains controversial. Herein, we describe a significant defect in the number of effector memory (EM) phenotype cells in ICOS(-/-) and ICOSL(-/-) mice that becomes progressively more dramatic as the mice age. This decrease was not due to a defect in the homeostatic proliferation of EM phenotype CD4 T cells in ICOS(-/-) or ICOSL(-/-) mice. To determine whether ICOS regulated the development or survival of EM CD4 T cells, we utilized an adoptive transfer model. We found no defect in development of EM CD4 T cells, but long-term survival of ICOS(-/-) EM CD4 T cells was significantly compromised compared to wild-type cells. The defect in survival was specific to EM cells as the central memory (CM) ICOS(-/-) CD4 T cells persisted as well as wild type cells. To determine the physiological consequences of a specific defect in EM CD4 T cells, wild-type and ICOS(-/-) mice were infected with influenza virus. ICOS(-/-) mice developed significantly fewer influenza-specific EM CD4 T cells and were more susceptible to re-infection than wild-type mice. Collectively, our findings demonstrate a role for ICOS costimulation in the maintenance of EM but not CM CD4 T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Swain SL, Dutton RW, Woodland DL. T cell responses to influenza virus infection: effector and memory cells. Viral Immunol. 2004;17:197–209. - PubMed
-
- Xu R, Johnson AJ, Liggitt D, Bevan MJ. Cellular and humoral immunity against vaccinia virus infection of mice. J Immunol. 2004;172:6265–6271. - PubMed
-
- Palmer DR, Krzych U. Cellular and molecular requirements for the recall of IL-4-producing memory CD4(+)CD45RO(+)CD27(-) T cells during protection induced by attenuated Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:652–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

