Large novel deletions detected in Chinese families with aniridia: correlation between genotype and phenotype
- PMID: 21364908
- PMCID: PMC3044699
Large novel deletions detected in Chinese families with aniridia: correlation between genotype and phenotype
Abstract
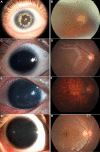
Purpose: To describe the clinical and genetic findings in two Chinese families with aniridia and other ocular abnormalities.
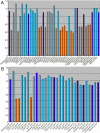
Methods: Two unrelated families were examined clinically. After informed consent was obtained, genomic DNA was extracted from the venous blood of all participants. Mutation screening of all exons of the PAX6 (paired box gene 6) gene was performed by direct sequencing of PCR-amplified DNA fragments. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) was performed to detect large deletions. Linkage analysis was used to validate the large deletions revealed by MLPA in all available family members.
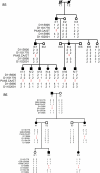
Results: Clinical examination and pedigree analysis revealed one four-generation family (85) and one three- generation family (86) with total aniridia, congenital cataracts, foveal hypoplasia, and glaucoma. No mutation in PAX6 was identified after PCR-sequencing. Through MLPA analysis, a large deletion including the whole PAX6 gene, DKFZp686k1684 (hypothetical LOC440034), and the RCN1 (reticulocalbin 1) gene was detected in family 85; a 3' deletion to the PAX6 gene including the ELP4 (elongator complex protein 4) and the DCDC1 (doublecortin domain containing 1) gene was identified in family 86.The two large deletions were confirmed with linkage analysis and the "loss of heterozygous" in the different PAX6 regions were co-segregated with the phenotype of the two families, respectively.
Conclusions: Patients with the PAX6 contiguous gene deletion, including the RCN1 gene, presented more severe vision impairments than those carrying the PAX6 3' deletion. Large deletions may account for several Chinese families and sporadic cases with aniridia and screening for these kinds of alterations should be included in aniridia patients' analyses.
Figures
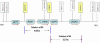
Similar articles
-
A 556 kb deletion in the downstream region of the PAX6 gene causes familial aniridia and other eye anomalies in a Chinese family.Mol Vis. 2011 Feb 10;17:448-55. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21321669 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation spectrum of PAX6 in Chinese patients with aniridia.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2139-47. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21850189 Free PMC article.
-
Two novel mutations of the PAX6 gene causing different phenotype in a cohort of Chinese patients.Eye (Lond). 2011 Dec;25(12):1581-9. doi: 10.1038/eye.2011.215. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Eye (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21904390 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 3' deletion results in aniridia, autism and mental retardation.Hum Genet. 2008 May;123(4):371-8. doi: 10.1007/s00439-008-0484-x. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18322702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aniridia due to a novel microdeletion affecting PAX6 regulatory enhancers: case report and review of the literature.J Genet. 2018 Jun;97(2):555-562. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 29932076 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Exome Sequencing of Congenital Cataracts Related Genes: Broadening the Mutation Spectrum and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in 27 Chinese Han Families.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 27;7(1):1219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01182-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28450710 Free PMC article.
-
Submicroscopic 11p13 deletion including the elongator acetyltransferase complex subunit 4 gene in a girl with language failure, intellectual disability and congenital malformations: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Nov 6;8(21):5296-5303. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5296. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33269262 Free PMC article.
-
A novel 11p13 microdeletion encompassing PAX6 in a Chinese Han family with aniridia, ptosis and mental retardation.Mol Cytogenet. 2015 Jan 22;8(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13039-015-0110-2. eCollection 2015. Mol Cytogenet. 2015. PMID: 25628759 Free PMC article.
-
11p13 deletions can be more frequent than the PAX6 gene point mutations in Polish patients with aniridia.J Appl Genet. 2013 Aug;54(3):345-51. doi: 10.1007/s13353-013-0154-0. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23761016 Free PMC article.
-
Screening, genetics, risk factors, and treatment of neonatal cataracts.Birth Defects Res. 2017 Jun 1;109(10):734-743. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1050. Epub 2017 May 22. Birth Defects Res. 2017. PMID: 28544770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee H, Khan R, O’Keefe M. Aniridia: current pathology and management. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008;86:708–15. - PubMed
-
- Ton CC, Hirvonen H, Miwa H, Weil MM, Monaghan P, Jordan T, van Heyningen V, Hastie ND, Meijers-Heijboer H, Drechsler M, Royer-Pokora B, Collins F, Swaroop A, Strong LC, Saunders GF. Positional cloning and characterization of a paired box- and homeobox-containing gene from the aniridia region. Cell. 1991;67:1059–74. - PubMed
-
- Glaser T, Walton DS, Maas RL. Genomic structure, evolutionary conservation and aniridia mutations in the human PAX6 gene. Nat Genet. 1992;2:232–9. - PubMed
-
- Prosser J, van Heyningen V. PAX6 mutations reviewed. Hum Mutat. 1998;11:93–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
