Chronic rhinosinusitis as a multifactorial inflammatory disorder
- PMID: 21365379
- PMCID: PMC4372071
- DOI: 10.1007/s11908-011-0166-z
Chronic rhinosinusitis as a multifactorial inflammatory disorder
Abstract
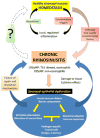
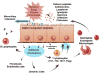
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a prevalent health condition characterized by sinonasal mucosal inflammation lasting at least 12 weeks. Heterogeneous in clinical presentation, histopathology, and therapeutic response, CRS represents a spectrum of disease entities with variable pathophysiology. Increased knowledge of cellular and molecular derangements in CRS suggests potential etiologies and targets for therapy. Microbial elements including fungi, staphylococcal enterotoxin, and biofilms have been implicated as inflammatory stimuli, along with airborne irritants and allergens. Defects in innate immunity have gained increased attention as contributors to the chronic inflammatory state. A combination of host susceptibility and environmental exposure is widely believed to underlie CRS, although direct evidence is lacking. Presently, without precise disease definitions and identifiable universal triggers, CRS pathogenesis is broadly described as multifactorial. Current research is beginning to unravel complex and diverse effects of chronic inflammation on sinonasal mucosal homeostasis, but dysfunctional pathways of inflammatory regulation and resolution require further elucidation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA, et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129(3 Suppl):S1–S32. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens W, Lund V, Mullol J. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2007. Rhinol Suppl. 2007;20:1–136. - PubMed
-
- Lethbridge-Cejku M, Schiller JS, Bernadel L. Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2002. Vital Health Stat. 2004 Jul;10(222):1–151. - PubMed
-
- Benninger MS, Sedory Holzer SE, Lau J. Diagnosis and treatment of uncomplicated acute bacterial rhinosinusitis: summary of the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research evidence-based report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;122(1):1–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

