The influence of objects on place field expression and size in distal hippocampal CA1
- PMID: 21365714
- PMCID: PMC3314262
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.20929
The influence of objects on place field expression and size in distal hippocampal CA1
Abstract
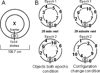
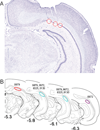
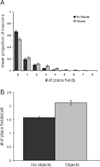
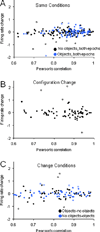
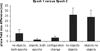
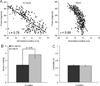
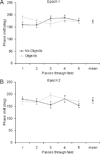
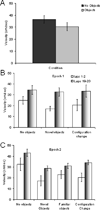
The perirhinal and lateral entorhinal cortices send prominent projections to the portion of the hippocampal CA1 subfield closest to the subiculum, but relatively little is known regarding the contributions of these cortical areas to hippocampal activity patterns. The anatomical connections of the lateral entorhinal and perirhinal cortices, as well as lesion data, suggest that these brain regions may contribute to the perception of complex stimuli such as objects. The current experiments investigated the degree to which three-dimensional objects affect place field size and activity within the distal region (closest to the subiculum) of CA1. The activity of CA1 pyramidal cells was monitored as rats traversed a circular track that contained no objects in some conditions and three-dimensional objects in other conditions. In the area of CA1 that receives direct lateral entorhinal input, three factors differentiated the objects-on-track conditions from the no-object conditions: more pyramidal cells expressed place fields when objects were present, adding or removing objects from the environment led to partial remapping in CA1, and the size of place fields decreased when objects were present. In addition, a proportion of place fields remapped under conditions in which the object locations were shuffled, which suggests that at least some of the CA1 neurons' firing patterns were sensitive to a particular object in a particular location. Together, these data suggest that the activity characteristics of neurons in the areas of CA1 receiving direct input from the perirhinal and lateral entorhinal cortices are modulated by non-spatial sensory input such as three-dimensional objects. © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Object and place information processing by CA1 hippocampal neurons of C57BL/6J mice.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Mar 1;123(3):1247-1264. doi: 10.1152/jn.00278.2019. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32023149 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of the immediate-early gene Arc in CA1 of the hippocampus reveals activity differences along the proximodistal axis that are attenuated by advanced age.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 20;33(8):3424-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4727-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23426670 Free PMC article.
-
CA1-projecting subiculum neurons facilitate object-place learning.Nat Neurosci. 2019 Nov;22(11):1857-1870. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0496-y. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Nat Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31548723 Free PMC article.
-
[Involvement of trisynaptic hippocampal pathway in generation of neural representations of object-place associations (analytical review)].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2009 Nov-Dec;59(6):643-59. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2009. PMID: 20120726 Review. Russian.
-
Allocentric representations of space in the hippocampus.Neurosci Res. 2020 Apr;153:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31276699 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a circuit-level understanding of hippocampal CA1 dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease across anatomical axes.J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism. 2018;8(1):412. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism. 2018. PMID: 29928558 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic integrative properties of dorsal CA1 pyramidal neuron subpopulations.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Mar 1;123(3):980-992. doi: 10.1152/jn.00397.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 22. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31967926 Free PMC article.
-
Nonuniform allocation of hippocampal neurons to place fields across all hippocampal subfields.Hippocampus. 2016 Oct;26(10):1328-44. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22609. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 27273259 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the Lateral Entorhinal Area Increases the Influence of Visual Cues on Hippocampal Place Cell Activity.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 May 29;11:40. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00040. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28611603 Free PMC article.
-
Top-down control of hippocampal signal-to-noise by prefrontal long-range inhibition.Cell. 2022 Apr 28;185(9):1602-1617.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.001. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35487191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaral D, Witter M. Hippocampal Formation. In: G P, editor. The Rat Nervous System. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 443–486.
-
- Brown JE, Skaggs WE. Concordant and discordant coding of spatial location in populations of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88(4):1605–1613. - PubMed
-
- Brun VH, Leutgeb S, Wu HQ, Schwarcz R, Witter MP, Moser EI, Moser MB. Impaired spatial representation in CA1 after lesion of direct input from entorhinal cortex. Neuron. 2008;57(2):290–302. - PubMed
-
- Burgess N, O'Keefe J. Neuronal computations underlying the firing of place cells and their role in navigation. Hippocampus. 1996;6(6):749–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

