Inhaled hypertonic saline in infants and toddlers with cystic fibrosis: short-term tolerability, adherence, and safety
- PMID: 21365779
- PMCID: PMC3107859
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.21425
Inhaled hypertonic saline in infants and toddlers with cystic fibrosis: short-term tolerability, adherence, and safety
Abstract
Background: Inhaled hypertonic saline (HS) is an attractive agent for chronic maintenance therapy in infants and toddlers with cystic fibrosis (CF) because it improves defective mucociliary clearance. Prior to undertaking a clinical trial of HS efficacy in young children with CF, tolerability, adherence, and safety must be established.
Methods: Three-center, open label evaluation of the short-term tolerability, adherence, and safety of 7% HS administered twice daily for 14 days in children with CF 12-30 months of age. The primary objective was to evaluate the proportion of participants unable to tolerate single and repeated doses of 7% HS according to protocol-defined criteria. Participants inhaled a test dose of HS at the enrollment visit; test dose intolerance was defined as fulfillment of at least one of 4 criteria. Participants who tolerated the test dose inhaled 7% HS twice daily for 14±2 days.
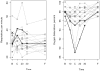
Results: Twenty children were enrolled. One was withdrawn due to maternal concern over fussiness with application of the facemask for the test dose. Of the 19 participants administered the test dose, 1 was withdrawn due to test dose intolerance (5%, 95% confidence interval 0, 26%). Eighteen participants completed the study; 1 was intolerant (95% CI 0, 27%) at the final visit due to new wheezes on exam in association with an upper respiratory infection and otitis media. Home symptom diaries demonstrated cough as the main symptom in the hour following inhalation, which decreased in frequency over the study period. Adherence as assessed by daily home diary and returned study drug ampoules was high. Participants reported receiving both treatments on a median of 100% of days; a median of 25 ampoules were used during a median of 13 days.
Conclusions: 7% HS appears well tolerated for up to 14 days in infants and toddlers with CF, with high adherence. These results provide encouraging short-term tolerability and adherence data for future trials assessing the safety and efficacy of 7% HS in young children with CF.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ratjen F, Doring G. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 2003;361:681–689. - PubMed
-
- Gibson RL, Burns JL, Ramsey BW. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168(8):918–951. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld M, Gibson RL, McNamara S, Emerson J, Burns JL, Castile R, Hiatt P, McCoy K, Wilson CB, Inglis A, Smith A, Martin TR, Ramsey BW. Early pulmonary infection, inflammation, and clinical outcomes in infants with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001;32(5):356–366. - PubMed
-
- Ranganathan SC, Stocks J, Dezateux C, Bush A, Wade A, Carr S, Castle R, Dinwiddie R, Hoo AF, Lum S, Price J, Stroobant J, Wallis C. The evolution of airway function in early childhood following clinical diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169(8):928–933. - PubMed
-
- Pillarisetti N, Linnane B, Ranganathan S. Early bronchiectasis in cystic fibrosis detected by surveillance CT. Respirology. 15(6):1009–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

