Serum uric acid distribution according to SLC22A12 W258X genotype in a cross-sectional study of a general Japanese population
- PMID: 21366895
- PMCID: PMC3060108
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-33
Serum uric acid distribution according to SLC22A12 W258X genotype in a cross-sectional study of a general Japanese population
Abstract
Background: Although SLC22A12 258X allele was found among those with hypouricemia, it was unknown that serum uric acid distribution among those with SLC22A12 258X allele. This study examined serum uric acid (SUA) distribution according to SLC22A12 W258X genotype in a general Japanese population.
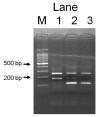
Methods: Subjects were 5,023 health checkup examinees (3,413 males and 1,610 females) aged 35 to 69 years with creatinine <2.0 mg/dL, who were participants of a cohort study belonging to the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study (J-MICC Study). SLC22A12 W258X was genotyped with a polymerase chain reaction with confronting two-pair primers.
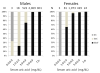
Results: The genotype frequency was 4,793 for WW, 225 for WX, and 5 for XX, which was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (p=0.164) with X allele 0.023 (95% confidence interval [0.021-0.027]). Mean (range) SUA was 6.2 (2.1-11.4) mg/dL for WW, 3.9 (0.8-7.8) mg/dL for WX, and 0.8 (0.7-0.9) mg/dL for XX among males, and 4.5 (1.9-8.9) mg/dL, 3.3 (2.0-6.5) mg/dL, and 0.60 (0.5-0.7) mg/dL among females, respectively. Six individuals with SUA less than 1.0 mg/dL included two males with XX genotype, one male with WX genotype, and three females with XX genotype. Subjects with WX genotype were 14 (77.8%) of 18 males with a SUA of 1.0-2.9 mg/dL, and 28 (34.6%) of 81 females with the same range of SUA. The corresponding values were 131 (25.1%) of 522 males and 37 (3.5%) of 1,073 females for SUA 3.0-4.9 mg/dL, and 8 (0.4%) of 2,069 males and 5 (1.1%) of 429 females for SUA 5.0-6.9 mg/dL. The X allele effect for SUA less than 3 mg/dL was significantly (p<0.001) higher in males (OR=102.5, [33.9-309.8]) than in females (OR = 25.6 [14.4-45.3]).
Conclusions: Although SLC22A12 W258X was a determining genetic factor on SUA, SUA of those with WX genotype distributed widely from 0.8 mg/dL to 7.8 mg/dL. It indicated that other genetic traits and/or lifestyle affected SUA of those with WX genotype, as well as those with WW genotype.
© 2011 Hamajima et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SLC22A12 W258X frequency according to serum uric acid level among Japanese health checkup examinees.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2011 Feb;73(1-2):41-8. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21614936 Free PMC article.
-
No association between MTHFR C677T and serum uric acid levels among Japanese with ABCG2 126QQ and SLC22A12 258WW.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2013 Feb;75(1-2):93-100. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23544272 Free PMC article.
-
Significant association of serum uric acid levels with SLC2A9 rs11722228 among a Japanese population.Mol Genet Metab. 2011 Aug;103(4):378-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Mol Genet Metab. 2011. PMID: 21511506
-
Analysis of mutations in the urate transporter 1 (URAT1) gene of Japanese patients with hypouricemia in northern Japan and review of the literature.Ren Fail. 2006;28(3):223-7. doi: 10.1080/08860220600580365. Ren Fail. 2006. PMID: 16703794 Review.
-
Renal hypouricemia in a recipient of living-donor kidney transplantation: a case report and literature review.CEN Case Rep. 2022 May;11(2):177-183. doi: 10.1007/s13730-021-00647-1. Epub 2021 Sep 23. CEN Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 34554426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Rare Variants Affecting Multiple Pathways in Japanese Patients with Palindromic Rheumatism.Kobe J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 30;70(1):E26-E38. doi: 10.24546/0100489391. Kobe J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38719338 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Basis of the Epidemiological Features and Clinical Significance of Renal Hypouricemia.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 13;10(7):1696. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071696. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A population-specific low-frequency variant of SLC22A12 (p.W258*) explains nearby genome-wide association signals for serum uric acid concentrations among Koreans.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0231336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231336. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271837 Free PMC article.
-
Non-urate transporter 1, non-glucose transporter member 9-related renal hypouricemia and acute renal failure accompanied by hyperbilirubinemia after anaerobic exercise: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Nov 26;20(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1618-1. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31771519 Free PMC article.
-
ASSOCIATIONS BETWEEN BODY MASS INDEX AND SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS IN A JAPANESE POPULATION WERE SIGNIFICANTLY MODIFIED BY LRP2 rs2544390.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2014 Aug;76(3-4):333-9. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25741042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benedek TG. Correlations of serum uric acid and lipid concentrations in normal, gouty, and atherosclerotic men. Ann Intern Med. 1967;66:851–861. - PubMed
-
- Alderman M. Uric acid in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Can J Cardiol. 1999;15(Suppl F):20F–22F. - PubMed
-
- Rathmann W, Funkhouser E, Dyer AR, Roseman JM. Relations of hyperuricemia with the various components of the insulin resistance syndrome in young black and white adults: the CARDIA study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults. Ann Epidemiol. 1998;8:250–261. doi: 10.1016/S1047-2797(97)00204-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

