Disruption of functional connectivity of the default-mode network in alcoholism
- PMID: 21368086
- PMCID: PMC3169657
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq297
Disruption of functional connectivity of the default-mode network in alcoholism
Abstract
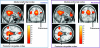
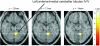
The default mode network (DMN) comprises brain structures maximally active at rest. Disturbance of network nodes or their connections occurs with some neuropsychiatric conditions and may underlie associated dysfunction. DMN connectivity has not been examined in alcoholism, which is marked by compromised DMN nodes and impaired spatial working memory. To test whether performance would be related to DMN integrity, we examined DMN functional connectivity using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data and graph theory analysis. We assumed that disruption of short paths between network nodes would attenuate processing efficiency. Alcoholics and controls were scanned at rest and during a spatial working memory task. At rest, the spontaneous slow fluctuations of fMRI signals in the posterior cingulate and cerebellar regions in alcoholics were less synchronized than in controls, indicative of compromised functional connectivity. Graph theory analysis indicated that during rest, alcoholics had significantly lower efficiency indices than controls between the posterior cingulate seed and multiple cerebellar sites. Greater efficiency in several connections correlated with longer sobriety in alcoholics. During the task, on which alcoholics performed on par with controls, connectivity between the left posterior cingulate seed and left cerebellar regions was more robust in alcoholics than controls and suggests compensatory networking to achieve normal performance.
Figures


References
-
- Allen G, McColl R, Barnard H, Ringe WK, Fleckenstein J, Cullum CM. Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar-prefrontal and cerebellar-parietal functional connectivity. NeuroImage. 2005;28:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Audoin B, Au Duong MV, Malikova I, Confort-Gouny S, Ibarrola D, Cozzone PJ, Pelletier J, Ranjeva JP. Functional magnetic resonance imaging and cognition at the very early stage of MS. J Neurol Sci. 2006;245:87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

