Balanced NMDA receptor activity in dopamine D1 receptor (D1R)- and D2R-expressing medium spiny neurons is required for amphetamine sensitization
- PMID: 21368124
- PMCID: PMC3054029
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1101424108
Balanced NMDA receptor activity in dopamine D1 receptor (D1R)- and D2R-expressing medium spiny neurons is required for amphetamine sensitization
Abstract
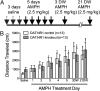
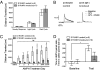
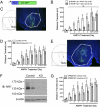
Signaling through N-methyl-D-aspartate-type glutamate receptors (NMDARs) is essential for the development of behavioral sensitization to psychostimulants such as amphetamine (AMPH). However, the cell type and brain region in which NMDAR signaling is required for AMPH sensitization remain unresolved. Here we use selective inactivation of Grin1, the gene encoding the essential NR1 subunit of NMDARs, in dopamine neurons or their medium spiny neuron (MSN) targets, to address this issue. We show that NMDAR signaling in dopamine neurons is not required for behavioral sensitization to AMPH. Conversely, removing NMDARs from MSNs that express the dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) significantly attenuated AMPH sensitization, and conditional, virus-mediated restoration of NR1 in D1R neurons in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of these animals rescued sensitization. Interestingly, sensitization could also be restored by virus-mediated inactivation of NR1 in all remaining neurons in the NAc of animals lacking NMDARs on D1R neurons, or by removing NMDARs from all MSNs. Taken together, these data indicate that unbalanced loss of NMDAR signaling in D1R MSNs alone prevents AMPH sensitization, whereas a balanced loss of NMDARs from both D1R and dopamine D2 receptor-expressing (D2R) MSNs is permissive for sensitization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential roles of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-containing neurons of the nucleus accumbens shell in behavioral sensitization.J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(6):1232-41. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13380. Epub 2015 Oct 28. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26442961
-
Chemokine receptor CCR2 contributes to neuropathic pain and the associated depression via increasing NR2B-mediated currents in both D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-containing medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens shell.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Oct;43(11):2320-2330. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0115-8. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29993042 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Calcium Signaling in D1 Receptor-Expressing Neurons of the Nucleus Accumbens Regulates Molecular, Cellular, and Behavioral Adaptations to Cocaine.Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;98(1):34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2025.01.013. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39864789
-
Potential for targeting dopamine/DARPP-32 signaling in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Mar;21(3):259-272. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1279149. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28052701 Review.
-
Reward signals downstream of dopamine D1 receptors.Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016 Dec;51(6):371-381. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 30461245 Review. English, Japanese.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of the RIIβ subunit of PKA affects locomotor activity and energy homeostasis in distinct neuronal populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 23;110(17):E1631-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219542110. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23569242 Free PMC article.
-
Tonic inhibition of accumbal spiny neurons by extrasynaptic α4βδ GABAA receptors modulates the actions of psychostimulants.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 15;34(3):823-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3232-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24431441 Free PMC article.
-
Corticostriatal plasticity in the nucleus accumbens core.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Dec;97(12):1559-1578. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24494. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 31298422 Free PMC article.
-
Selective alterations of NMDAR function and plasticity in D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens shell following chronic intermittent ethanol exposure.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jan;112(Pt A):164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 26946430 Free PMC article.
-
A single-nucleus transcriptomic atlas of medium spiny neurons in the rat nucleus accumbens.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 6;14(1):18258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69255-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39107568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robinson TE, Berridge KC. Addiction. Annu Rev Psychol. 2003;54:25–53. - PubMed
-
- Robinson TE, Jurson PA, Bennett JA, Bentgen KM. Persistent sensitization of dopamine neurotransmission in ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens) produced by prior experience with (+)-amphetamine: A microdialysis study in freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1988;462:211–222. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MJ, Beurrier C, Bonci A, Malenka RC. Long-term depression in the nucleus accumbens: A neural correlate of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:1217–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

