Interconversions of P and F intermediates of cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans
- PMID: 21368144
- PMCID: PMC3053992
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1100950108
Interconversions of P and F intermediates of cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans
Abstract
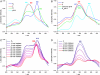
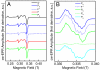
Cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) is the terminal enzyme of the respiratory chain. This redox-driven proton pump catalyzes the four-electron reduction of molecular oxygen to water, one of the most fundamental processes in biology. Elucidation of the intermediate structures in the catalytic cycle is crucial for understanding both the mechanism of oxygen reduction and its coupling to proton pumping. Using CcO from Paracoccus denitrificans, we demonstrate that the artificial F state, classically generated by reaction with an excess of hydrogen peroxide, can be converted into a new P state (in contradiction to the conventional direction of the catalytic cycle) by addition of ammonia at pH 9. We suggest that ammonia coordinates directly to Cu(B) in the binuclear active center in this P state and discuss the chemical structures of both oxoferryl intermediates F and P. Our results are compatible with a superoxide bound to Cu(B) in the F state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resonance Raman characterization of the ammonia-generated oxo intermediate of cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans.Biochemistry. 2013 Sep 10;52(36):6197-202. doi: 10.1021/bi400535m. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23914722
-
Kinetic resolution of a tryptophan-radical intermediate in the reaction cycle of Paracoccus denitrificans cytochrome c oxidase.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 26;282(43):31580-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705520200. Epub 2007 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17761680
-
The role of tryptophan 272 in the Paracoccus denitrificans cytochrome c oxidase.FEBS Lett. 2006 Feb 20;580(5):1345-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.054. Epub 2006 Jan 26. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16460733
-
Respiratory conservation of energy with dioxygen: cytochrome C oxidase.Met Ions Life Sci. 2015;15:89-130. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12415-5_4. Met Ions Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25707467 Review.
-
Cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans. Protein, chemical, structural, and evolutionary aspects.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1991 Apr;23(2):269-89. doi: 10.1007/BF00762222. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1991. PMID: 1646797 Review.
Cited by
-
How hydrogen peroxide is metabolized by oxidized cytochrome c oxidase.Biochemistry. 2014 Jun 10;53(22):3564-75. doi: 10.1021/bi401078b. Epub 2014 May 30. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24840065 Free PMC article.
-
Two tyrosyl radicals stabilize high oxidation states in cytochrome C oxidase for efficient energy conservation and proton translocation.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Mar 14;134(10):4753-61. doi: 10.1021/ja210535w. Epub 2012 Mar 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22296274 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic identification of the catalytic intermediates of cytochrome c oxidase in respiring heart mitochondria.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2023 Apr 1;1864(2):148934. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2022.148934. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2023. PMID: 36379270 Free PMC article.
-
In Escherichia coli Ammonia Inhibits Cytochrome bo3 But Activates Cytochrome bd-I.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 25;10(1):13. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010013. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375541 Free PMC article.
-
Copper active sites in biology.Chem Rev. 2014 Apr 9;114(7):3659-853. doi: 10.1021/cr400327t. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24588098 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gennis RB. Coupled proton and electron transfer reactions in cytochrome oxidase. Front Biosci. 2004;9:581–591. - PubMed
-
- Brzezinski P, Larsson G. Redox-driven proton pumping by heme-copper oxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1605:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Wikström M, Morgan JE. The dioxygen cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10266–10273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

