Asparagine repeat function in a Plasmodium falciparum protein assessed via a regulatable fluorescent affinity tag
- PMID: 21368162
- PMCID: PMC3060247
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018449108
Asparagine repeat function in a Plasmodium falciparum protein assessed via a regulatable fluorescent affinity tag
Abstract
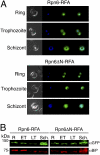
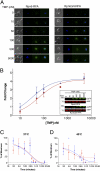
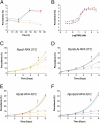
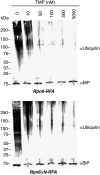
One in four proteins in Plasmodium falciparum contains asparagine repeats. We probed the function of one such 28-residue asparagine repeat present in the P. falciparum proteasome lid subunit 6, Rpn6. To aid our efforts, we developed a regulatable, fluorescent affinity (RFA) tag that allows cellular localization, manipulation of cellular levels, and affinity isolation of a chosen protein in P. falciparum. The tag comprises a degradation domain derived from Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase together with GFP. The expression of RFA-tagged proteins is regulated by the simple folate analog trimethoprim (TMP). Parasite lines were generated in which full-length Rpn6 and an asparagine repeat-deletion mutant of Rpn6 were fused to the RFA tag. The knockdown of Rpn6 upon removal of TMP revealed that this protein is essential for ubiquitinated protein degradation and for parasite survival, but the asparagine repeat is dispensable for protein expression, stability, and function. The data point to a genomic mechanism for repeat perpetuation rather than a positive cellular role. The RFA tag should facilitate study of the role of essential genes in parasite biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Breman JG. The ears of the hippopotamus: Manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64(Suppl1–2):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Singh GP, et al. Hyper-expansion of asparagines correlates with an abundance of proteins with prion-like domains in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004;137:307–319. - PubMed
-
- DePristo MA, Zilversmit MM, Hartl DL. On the abundance, amino acid composition, and evolutionary dynamics of low-complexity regions in proteins. Gene. 2006;378:19–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

